Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Radiomics Model Predicting Lymph Node Status in Operable Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 32373511
- PMCID: PMC7179686
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00464
Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Radiomics Model Predicting Lymph Node Status in Operable Cervical Cancer
Abstract
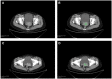
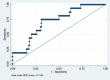
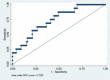
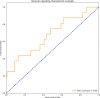
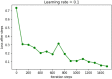
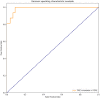
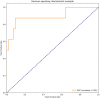
Aim: To develop and validate a deep learning radiomics model, which could predict the lymph node metastases preoperatively in cervical cancer patients. Patients and methods: We included a cohort of 226 pathological proven operable cervical cancer patients in two academic medical institutions from December 2014 to November 2017. Then this dataset was split into training set (n = 176) and independent testing set (n = 50) randomly. Five radiomic features were selected and a radiomic signature was established. We then combined these five radiomic features with the preoperative tumor histology and grade of these patients together. Baseline logistic regression model (LRM) and support vector machine model (SVM) were established for the comparison. We then explored the performance of a deep neural network (DNN), which is a popular deep learning model nowadays. Finally, performance of this DNN was validated in another independent test set including 50 cases of operable cervical cancer patients. Results: One thousand forty-five radiomic features were extracted for each patient. Twenty-eight features were found to be significantly correlated with the lymph node status in these patients (P < 0.05). Five radiomic features were further selected for further study due to their higher predictive powers. Baseline LRM incorporating these five radiomic and two clinicopathological features was established, which had an area under receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) of 0.7372 and an accuracy of 89.20%. The established DNN model had four neural layers, in which layer there were 10 neurons. Adagrad optimizer and 1,500 iterations were used in training. The trained DNN had an area under curve (AUC) of 0.99 and an accuracy of 97.16% in the internal validation. To exclude the overfitting, independent external validation was also performed. AUC and accuracy in test set could still retain 0.90 and 92.00% respectively. Conclusion: This study used deep learning method to provide a comprehensive predictive model using preoperative CT images, tumor histology, and grade in cervical cancer patients. This model showed an acceptable accuracy in the prediction of lymph node status in cervical cancer. Our model may help identifying those patients who could benefit a lot from radiation therapy rather than primary hysterectomy surgery if this model could resist strict testing of future randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Keywords: cervical cancer; deep learning; deep neural network; lymph node status; radiomics.
Copyright © 2020 Dong, Yang, Cui, Zhang, Sun, Song, Wang, Kong and Yang.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Magnetic resonance imaging radiomics predicts preoperative axillary lymph node metastasis to support surgical decisions and is associated with tumor microenvironment in invasive breast cancer: A machine learning, multicenter study.EBioMedicine. 2021 Jul;69:103460. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103460. Epub 2021 Jul 4. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34233259 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Computed Tomography-Based Radiomics Model to Predict Central Cervical Lymph Node Metastases in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Multicenter Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 21;12:741698. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.741698. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34745008 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer by radiomic signatures from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Jan;49(1):131-140. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26224. Epub 2018 Sep 1. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30171822 Free PMC article.
-
The value of machine learning in preoperative identification of lymph node metastasis status in endometrial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 20;13:1289050. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1289050. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38173835 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of AI in Breast Cancer Lymph Node Classification: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 21;15(8):2400. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082400. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence radiomics in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of gynecological cancer: a literature review.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):2508-2532. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-618. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40386259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpretable Radiomic Signature for Breast Microcalcification Detection and Classification.J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 Jun;37(3):1038-1053. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01012-1. Epub 2024 Feb 13. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024. PMID: 38351223 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of lymph node status in patients with early-stage cervical cancer based on radiomic features of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images.BMC Med Imaging. 2023 Aug 1;23(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12880-023-01059-6. BMC Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37528338 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomic Score as a Potential Imaging Biomarker for Predicting Survival in Patients With Cervical Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 16;11:706043. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.706043. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34485139 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-algorithms analysis for pre-treatment prediction of response to transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma on multiphase MRI.Insights Imaging. 2023 Feb 28;14(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01380-2. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36854872 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

