Tumor Hypoxia: Impact on Radiation Therapy and Molecular Pathways
- PMID: 32373534
- PMCID: PMC7186437
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00562
Tumor Hypoxia: Impact on Radiation Therapy and Molecular Pathways
Abstract
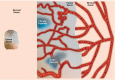
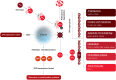
Tumor hypoxia is a common feature of the microenvironment in solid tumors, primarily due to an inadequate, and heterogeneous vascular network. It is associated with resistance to radiotherapy and results in a poorer clinical outcome. The presence of hypoxia in tumors can be identified by various invasive and non-invasive techniques, and there are a number of approaches by which hypoxia can be modified to improve outcome. However, despite these factors and the ongoing extensive pre-clinical studies, the clinical focus on hypoxia is still to a large extent lacking. Hypoxia is a major cellular stress factor and affects a wide range of molecular pathways, and further understanding of the molecular processes involved may lead to greater clinical applicability of hypoxic modifiers. This review is a discussion of the characteristics of tumor hypoxia, hypoxia-related molecular pathways, and the role of hypoxia in treatment resistance. Understanding the molecular aspects of hypoxia will improve our ability to clinically monitor hypoxia and to predict and modify the therapeutic response.
Keywords: gene regulation; hypoxia; hypoxia classifyer; intracellular signaling; radiation response.
Copyright © 2020 Sørensen and Horsman.
Figures
References
-
- Folkman J. How is blood vessel growth regulated in normal and neoplastic tissue? G.H.A. clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. (1986) 46:467–73. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

