Synergistic interactions of cadmium-free quantum dots embedded in a photosensitised polymer surface: efficient killing of multidrug-resistant strains at low ambient light levels
- PMID: 32373810
- PMCID: PMC7497474
- DOI: 10.1039/c9nr10421f
Synergistic interactions of cadmium-free quantum dots embedded in a photosensitised polymer surface: efficient killing of multidrug-resistant strains at low ambient light levels
Abstract
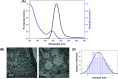
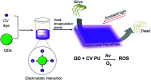
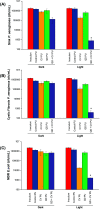
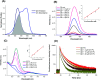
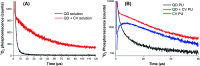
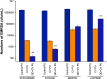
Cadmium-free quantum dots (QD) were combined with crystal violet photosensitising dye and incorporated into medical grade polyurethane via a non-covalent dipping process known as 'swell-encapsulation-shrink'. The antibacterial efficacy of the prepared quantum dot-crystal violet polyurethane substrates (QD + CV PU) was investigated under low power visible light illumination at similar intensities (500 lux) to those present in clinical settings. The antibacterial performance of QD + CV PU was superior to the constituent polymer substrates, eliminating ∼99.9% of an environmental P. aeruginosa strain, a clinical P. aeruginosa strain from a cystic fibrosis patient and a clinical E. coli strain. The nature of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) involved in antibacterial activity of the QD + CV PU surface was investigated using ROS inhibitors and time-resolved optical spectroscopy. The photo-physical interactions of the green-emitting QDs with CV lead to a combination of Type I and II electron transfer and energy transfer processes, with the highly potent ROS singlet oxygen playing a dominant role. This study is the first to demonstrate highly efficient synergistic killing of clinical and environmental strains of intrinsically resistant and multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria using light-activated surfaces containing biocompatible cadmium-free QDs and crystal violet dye at ambient light levels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Photoactivable Polymers Embedded with Cadmium-Free Quantum Dots and Crystal Violet: Efficient Bactericidal Activity against Clinical Strains of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Apr 3;11(13):12367-12378. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b02109. Epub 2019 Mar 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 30855136
-
Solubilization and bio-conjugation of quantum dots and bacterial toxicity assays by growth curve and plate count.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jul 11;(65):e3969. doi: 10.3791/3969. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22824953 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial phototoxicity of biomimetic CdTe-GSH quantum dots.J Appl Microbiol. 2021 Jul;131(1):155-168. doi: 10.1111/jam.14957. Epub 2020 Dec 18. J Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33274558
-
Isolating the Escherichia coli Transcriptomic Response to Superoxide Generation from Cadmium Chalcogenide Quantum Dots.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019 Sep 9;5(9):4206-4218. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01087. Epub 2019 Aug 7. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019. PMID: 33417778
-
Antibacterial Surfaces with Activity against Antimicrobial Resistant Bacterial Pathogens and Endospores.ACS Infect Dis. 2020 May 8;6(5):939-946. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00279. Epub 2020 Mar 11. ACS Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32126763
Cited by
-
Antipathogenic properties and applications of low-dimensional materials.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 23;12(1):3897. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23278-7. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34162835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric Materials with Antibacterial Activity: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;13(4):613. doi: 10.3390/polym13040613. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bisen P. S., Emerging epidemics: Management and Control, Wiley Blackwell, Hoboken, N.J., 2013.
-
- O'Neill J., Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations, 2016.
-
- Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013, Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 2013.
-
- Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Europe – Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) 2017, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), Stockholm, 2018.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

