Disruption of tight junctions contributes to hyposalivation of salivary glands in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 32374057
- PMCID: PMC7476205
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.13203
Disruption of tight junctions contributes to hyposalivation of salivary glands in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
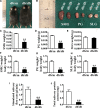
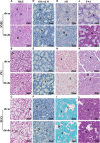
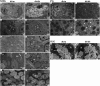
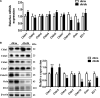
Tight junction (TJ) plays an important role in regulating paracellular fluid transport in salivary glands; however, little is known about the involvement of TJs in diabetes salivary glands. This study aimed to investigate the alterations of TJs and their possible contribution in diabetes-induced hyposalivation. Here, we observed that the morphologies of submandibular glands (SMGs) were impaired, characterized by enlarged acini accumulation with giant secretory granules, which were significantly reduced in atrophic ducts in SMGs of db/db mice, a spontaneous model of type-2 diabetes. However, the secretory granules were increased and scattered in the acini of diabetes parotid glands (PGs). Other ultrastructural damages including swollen mitochondria, expansive endoplasmic reticulum, and autophagosomes were observed in the diabetes group. The levels of TJ proteins including claudin-1 (Cldn1) and claudin-3 (Cldn3) were increased, whereas those of claudin-4 (Cldn4), occludin (Ocln), and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) were decreased in SMGs of db/db mice. Higher Cldn1 and Cldn3 and lower claudin-10 (Cldn10) and Ocln levels were observed in PGs of diabetes mice. Taken together, the structures of SMGs and PGs were impaired in diabetes mice, and the disruption of TJ integrity in both SMGs and PGs may contribute to diabetes-induced hyposalivation.
Keywords: diabetes; saliva; salivary gland; submandibular gland; tight junction.
© 2020 Anatomical Society.
Figures

References
-
- Amoozadeh, Y. , Dan, Q. , Anwer, S. , Huang, H.H. , Barbieri, V. , Waheed, F. et al. (2017) Tumor necrosis factor‐alpha increases claudin‐1, 4, and 7 expression in tubular cells: role in permeability changes. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 232, 2210–2220. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, L.C. and Garrett, J.R. (1986) Lipid accumulation in the major salivary glands of streptozotocin‐diabetic rats. Archives of Oral Biology, 31, 469–475. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, L.C. , Suleiman, A.H. and Garrett, J.R. (1994) Morphological effects of diabetes on the granular ducts and acini of the rat submandibular gland. Microscopy Research and Technique, 27, 61–70. - PubMed
-
- Beltrame de Oliveira, R. , Matheus, V.A. , Canuto, L.P. , De Sant'ana, A. and Collares‐Buzato, C.B. (2019) Time‐dependent alteration to the tight junction structure of distal intestinal epithelia in type 2 prediabetic mice. Life Sciences, 238, 116971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

