Implications of radiation microdosimetry for accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy: a radiobiological perspective
- PMID: 32374629
- PMCID: PMC7336073
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20200311
Implications of radiation microdosimetry for accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy: a radiobiological perspective
Abstract
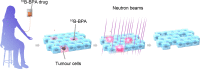
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) has great potential to selectively destroy cancer cells while sparing surrounding normal cells. The basic concept of BNCT was developed in the 1930s, but it has not yet been commonly used in clinical practice, even though there is now a large number of experimental and translational studies demonstrating its marked therapeutic potential. With the development of neutron accelerators that can be installed in medical institutions, accelerator-based BNCT is expected to become available at several medical institutes around the world in the near future. In this commentary, from the point of view of radiation microdosimetry, we discuss the biological effects of BNCT, especially the underlying mechanisms of compound biological effectiveness. Radiobiological perspectives provide insight into the effectiveness of BNCT in creating a synergy effect in the field of clinical oncology.
Figures
References
-
- Yoshino K, Suzuki A, Mori Y, Kakihana H, Honda C, Mishima Y, et al. Improvement of solubility of p-boronophenylalanine by complex formation with monosaccharides. Strahlenther Onkol 1989; 165(2-3): 127–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

