Thrombospondin-1 in maladaptive aging responses: a concept whose time has come
- PMID: 32374675
- PMCID: PMC7468894
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00089.2020
Thrombospondin-1 in maladaptive aging responses: a concept whose time has come
Abstract
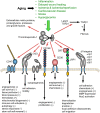
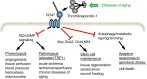
Numerous age-dependent alterations at the molecular, cellular, tissue and organ systems levels underlie the pathophysiology of aging. Herein, the focus is upon the secreted protein thrombospondin-1 (TSP1) as a promoter of aging and age-related diseases. TSP1 has several physiological functions in youth, including promoting neural synapse formation, mediating responses to ischemic and genotoxic stress, minimizing hemorrhage, limiting angiogenesis, and supporting wound healing. These acute functions of TSP1 generally require only transient expression of the protein. However, accumulating basic and clinical data reinforce the view that chronic diseases of aging are associated with accumulation of TSP1 in the extracellular matrix, which is a significant maladaptive contributor to the aging process. Identification of the relevant cell types that chronically produce and respond to TSP1 and the molecular mechanisms that mediate the resulting maladaptive responses could direct the development of therapeutic agents to delay or revert age-associated maladies.
Keywords: CD47; aging; cardiovascular and metabolic disease; self-renewal; senescence; thrombospondin-1.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S.I. serves as Chief Science Officer of Radiation Control Technologies, Inc. J.S.I. and D.D.R. are co-inventors of CD47 technology patents assigned to the United States of America.
Figures
References
-
- Aiken J, Mandel ER, Riddell MC, Birot O. Hyperglycaemia correlates with skeletal muscle capillary regression and is associated with alterations in the murine double minute-2/forkhead box O1/thrombospondin-1 pathway in type 1 diabetic BioBreeding rats. Diab Vasc Dis Res 16: 28–37, 2019. doi: 10.1177/1479164118805928. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

