A comprehensive analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 32374740
- PMCID: PMC7202610
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232272
A comprehensive analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
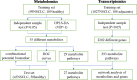
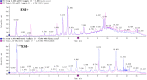
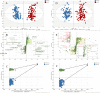
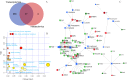
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains a leading cause of cancer death globally. More accurate and reliable diagnostic methods/biomarkers are urgently needed. Joint application of metabolomics and transcriptomics technologies possesses the high efficiency of identifying key metabolic pathways and functional genes in lung cancer patients. In this study, we performed an untargeted metabolomics analysis of 142 NSCLC patients and 159 healthy controls; 35 identified metabolites were significantly different between NSCLC patients and healthy controls, of which 6 metabolites (hypoxanthine, inosine, L-tryptophan, indoleacrylic acid, acyl-carnitine C10:1, and lysoPC(18:2)) were chosen as combinational potential biomarkers for NSCLC. The area under the curve (AUC) value, sensitivity (SE), and specificity (SP) of these six biomarkers were 0.99, 0.98, and 0.99, respectively. Potential diagnostic implications of the metabolic characteristics in NSCLC was studied. The metabolomics results were further verified by transcriptomics analysis of 1027 NSCLC patients and 108 adjacent peritumoral tissues from TCGA database. This analysis identified 2202 genes with significantly different expressions in cancer cells compared to normal controls, which in turn defined pathways implicated in the metabolism of the compounds revealed by metabolomics analysis. We built a fully connected network of metabolites and genes, which shows a good correspondence between the transcriptome analysis and the metabolites selected for diagnosis. In conclusion, this work provides evidence that the metabolic biomarkers identified may be used for NSCLC diagnosis and screening. Comprehensive analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics data offered a validated and comprehensive understanding of metabolism in NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Chen J, Brun T, Campbell TC, Li J, Geissler C, Li M. Epidemiology of lung cancer in China. Chinese Journal of Cancer Prevention & Treatment. 2015;6(2):209–15.
-
- Li Y, Song X, Zhao X, Zou L, Xu G. Serum metabolic profiling study of lung cancer using ultra high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry ☆. Journal of Chromatography B. 2014;966(Sp. Iss. SI):147–53. - PubMed
-
- Jin Y, Yang Y, Su Y, Ye X, Liu W, Yang Q, et al. Identification a novel clinical biomarker in early diagnosis of human non-small cell lung cancer 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

