Comparison of a human neuronal model proteome upon Japanese encephalitis or West Nile Virus infection and potential role of mosquito saliva in neuropathogenesis
- PMID: 32374750
- PMCID: PMC7202638
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232585
Comparison of a human neuronal model proteome upon Japanese encephalitis or West Nile Virus infection and potential role of mosquito saliva in neuropathogenesis
Abstract
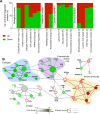
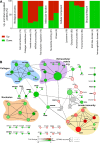
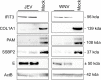
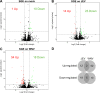
Neurotropic flavivirus Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and West Nile virus (WNV) are amongst the leading causes of encephalitis. Using label-free quantitative proteomics, we identified proteins differentially expressed upon JEV (gp-3, RP9) or WNV (IS98) infection of human neuroblastoma cells. Data are available via ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD016805. Both viruses were associated with the up-regulation of immune response (IFIT1/3/5, ISG15, OAS, STAT1, IRF9) and the down-regulation of SSBP2 and PAM, involved in gene expression and in neuropeptide amidation respectively. Proteins associated to membranes, involved in extracellular matrix organization and collagen metabolism represented major clusters down-regulated by JEV and WNV. Moreover, transcription regulation and mRNA processing clusters were also heavily regulated by both viruses. The proteome of neuroblastoma cells infected by JEV or WNV was significantly modulated in the presence of mosquito saliva, but distinct patterns were associated to each virus. Mosquito saliva favored modulation of proteins associated with gene regulation in JEV infected neuroblastoma cells while modulation of proteins associated with protein maturation, signal transduction and ion transporters was found in WNV infected neuroblastoma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- S H-J, N H, M H, MakiElin, W C, T BD, et al. Susceptibility of a North American Culex quinquefasciatus to Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases. Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. 140 Huguenot Street, 3rd Floor New Rochelle, NY 10801 USA; 2015;15: 709–711. 10.1089/vbz.2015.1821 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

