An assessment of the impacts of litter treatments on the litter quality and broiler performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32374780
- PMCID: PMC7202646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232853
An assessment of the impacts of litter treatments on the litter quality and broiler performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: The choice of the most suitable litter treatment should be based on scientific evidence. This systematic review assessed the effectiveness of litter treatments on ammonia concentration, pH, moisture and pathogenic microbiota of the litter and their effects on body weight, feed intake, feed conversion and mortality of broilers.
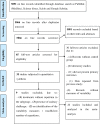
Methods: The systematic literature search was conducted using PubMed (Medline), Google Scholar, ScienceDirect and Scielo databases to retrieve articles published from January 1998 to august 2019. Means, standard deviations and sample sizes were extracted from each study. The response variables were analyzed using the mean difference (MD) or standardized mean difference (SMD), (litter treatment minus control group). All variables were analyzed using random effects meta-analyses.
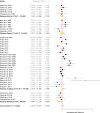
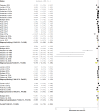
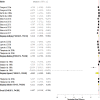
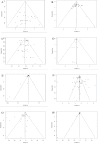
Results: Subgroup meta-analysis revealed that acidifiers reduce pH (P<0.001), moisture (P = 0.002) ammonia (P = 0.011) and pathogenic microbiota (P <0.001) of the litter and improves the weight gain (P = 0.019) and decreases the mortality rate of broilers (P<0.001) when compared with controls. Gypsum had a positive effect on ammonia reduction (P = 0.012) and improved feed conversion (P = 0.023). Alkalizing agents raise the pH (P = 0.035), worsen feed conversion (P<0.001), increase the mortality rate (P <0.001), decrease the moisture content (P<0.001) and reduce the pathogenic microbiota of the litter (P<0.001) once compared to controls. Superphosphate and adsorbents reduce, respectively, pH (P<0.001) and moisture (P = 0.007) of the litter compared to control groups.
Conclusion: None of the litter treatments influenced the feed intake of broilers. Meta-analyses of the selected studies showed positive and significant effects of the litter treatments on broiler performance and litter quality when compared with controls. Alkalizing was associated with worse feed conversion and high mortality of broilers.
Conflict of interest statement
The MADP received salary from Brasil Foods S/A. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. The other authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Dai Prá MA, Roll VFB. Cama de aviário: Utilização, reutilização e destino. 3ª ed. Porto Alegre: Evangraf; 2019.
-
- Vieira MFA. Caracterização e análise da qualidade sanitária de camas de frango de diferentes materiais reutilizados sequencialmente. M.Sc. Dissertação. Universidade Federal de Viçosa. 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

