Structural basis of the XPB-Bax1 complex as a dynamic helicase-nuclease machinery for DNA repair
- PMID: 32374860
- PMCID: PMC7293015
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa324
Structural basis of the XPB-Bax1 complex as a dynamic helicase-nuclease machinery for DNA repair
Abstract
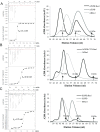
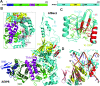
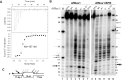
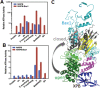
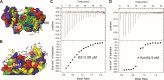
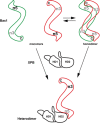
Nucleotide excision repair (NER) is a major DNA repair pathway for a variety of DNA lesions. XPB plays a key role in DNA opening at damage sites and coordinating damage incision by nucleases. XPB is conserved from archaea to human. In archaea, XPB is associated with a nuclease Bax1. Here we report crystal structures of XPB in complex with Bax1 from Archaeoglobus fulgidus (Af) and Sulfolobus tokodaii (St). These structures reveal for the first time four domains in Bax1, which interacts with XPB mainly through its N-terminal domain. A Cas2-like domain likely helps to position Bax1 at the forked DNA allowing the nuclease domain to incise one arm of the fork. Bax1 exists in monomer or homodimer but forms a heterodimer exclusively with XPB. StBax1 keeps StXPB in a closed conformation and stimulates ATP hydrolysis by XPB while AfBax1 maintains AfXPB in the open conformation and reduces its ATPase activity. Bax1 contains two distinguished nuclease active sites to presumably incise DNA damage. Our results demonstrate that protein-protein interactions regulate the activities of XPB ATPase and Bax1 nuclease. These structures provide a platform to understand the XPB-nuclease interactions important for the coordination of DNA unwinding and damage incision in eukaryotic NER.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

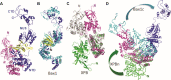
References
-
- Fan L., Arvai A.S., Cooper P.K., Iwai S., Hanaoka F., Tainer J.A.. Conserved XPB core structure and motifs for DNA unwinding: implications for pathway selection of transcription or excision repair. Mol. Cell. 2006; 22:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Ma X., Hong Y., Han W., Sheng D., Ni J., Hou G., Shen Y.. Single-stranded DNA binding activity of XPBI, but not XPBII, from Sulfolobus tokodaii causes double-stranded DNA melting. Extremophiles. 2011; 15:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Gulyas K.D., Donahue T.F.. SSL2, a suppressor of a stem-loop mutation in the HIS4 leader encodes the yeast homolog of human ERCC-3. Cell. 1992; 69:1031–1042. - PubMed
-
- Koken M.H., Vreeken C., Bol S.A., Cheng N.C., Jaspers-Dekker I., Hoeijmakers J.H., Eeken J.C., Weeda G., Pastink A.. Cloning and characterization of the Drosophila homolog of the xeroderma pigmentosum complementation-group B correcting gene, ERCC3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992; 20:5541–5548. - PMC - PubMed

