Antagonistic Center-Surround Mechanisms for Direction Selectivity in the Retina
- PMID: 32375036
- PMCID: PMC7221349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107608
Antagonistic Center-Surround Mechanisms for Direction Selectivity in the Retina
Abstract
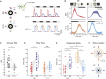
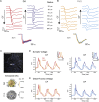
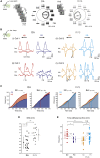
An antagonistic center-surround receptive field is a key feature in sensory processing, but how it contributes to specific computations such as direction selectivity is often unknown. Retinal On-starburst amacrine cells (SACs), which mediate direction selectivity in direction-selective ganglion cells (DSGCs), exhibit antagonistic receptive field organization: depolarizing to light increments and decrements in their center and surround, respectively. We find that a repetitive stimulation exhausts SAC center and enhances its surround and use it to study how center-surround responses contribute to direction selectivity. Center, but not surround, activation induces direction-selective responses in SACs. Nevertheless, both SAC center and surround elicited direction-selective responses in DSGCs, but to opposite directions. Physiological and modeling data suggest that the opposing direction selectivity can result from inverted temporal balance between excitation and inhibition in DSGCs, implying that SAC's response timing dictates direction selectivity. Our findings reveal antagonistic center-surround mechanisms for direction selectivity and demonstrate how context-dependent receptive field reorganization enables flexible computations.
Keywords: antagonistic center-surround; direction selective ganglion cells; direction selectivity; excitatory-inhibitory balance; neural circuits; neural computation; receptive field; retina; starburst amacrine cells; visual processing.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Allman J., Miezin F., McGuinness E. Stimulus specific responses from beyond the classical receptive field: neurophysiological mechanisms for local-global comparisons in visual neurons. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1985;8:407–430. - PubMed
-
- Briggman K.L., Helmstaedter M., Denk W. Wiring specificity in the direction-selectivity circuit of the retina. Nature. 2011;471:183–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

