The Impact of COVID-19 on European Health Care and Urology Trainees
- PMID: 32376133
- PMCID: PMC7183959
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.04.042
The Impact of COVID-19 on European Health Care and Urology Trainees
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has had rapid and inevitable effects on health care systems and the training and work plans of urology residents. Smart learning is a valuable strategy for maintaining the learning curve of residents.
Copyright © 2020 European Association of Urology. All rights reserved.
Figures
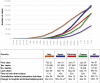
Comment in
-
Re: Karl H. Pang, Diego M. Carrion, Juan Gomez Rivas, et al. The Impact of COVID-19 on European Health Care and Urology Trainees.Eur Urol 2020:78;6-8.Eur Urol. 2020 Dec;78(6):e236. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.05.028. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Eur Urol. 2020. PMID: 32532516 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
-
- Marchalik D., Goldman C.C., Carvalho F.F.L. Resident burnout in USA and European urology residents: an international concern. BJU Int. 2019;124:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Worldometer. Coronavirus. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

