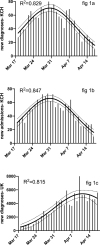
COVID-19 diagnoses in South East London peaked before the UK suggesting early measures reduced transmission
- PMID: 32376453
- PMCID: PMC7196558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.043
COVID-19 diagnoses in South East London peaked before the UK suggesting early measures reduced transmission
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; London; UK.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None of the authors have a conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- John Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Centrehttps://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed 24/04/2020).
-
- UK Gov website. https://www.gov.uk/guidance/coronavirus-covid-19-information-for-the-pub... (accessed 24/04/2020).
-
- Rothe C., Schunk M., Sothmann P., Bretzel G., Froeschl G., Wallrauch C., Zimmer T., Thiel V., Janke C., Guggemos W., Seilmaier M., Drosten C., Vollmar P., Zwirglmaier K., Zange S., Wölfel R., Hoelscher M. Transmission of 2019-nCoV infection from an asymptomatic contact in Germany. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:970–971. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., Guan L., Wei Y., Li H., Wu X., Xu J., Tu S., Zhang Y., Chen H., Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources