[Mechanism of Jiawei Huangqin decoction for treating ulcerative colitis in mice: the role of STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6 pathway]
- PMID: 32376533
- PMCID: PMC7086134
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.02.10
[Mechanism of Jiawei Huangqin decoction for treating ulcerative colitis in mice: the role of STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6 pathway]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the therapeutic effect of Jiawei Huangqin (JWHQ) decoction on ulcerative colitis (UC) and the regulation of STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6 pathway.
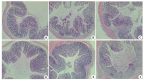
Methods: Forty-eight mice were randomized into blank control group, model group, positive control (Sulfasalazine) group, and low-, moderate- and high-dose JWHQ Decoction groups (n=8). In all but the blank control groups, the mice were given 3% DSS in drinking water to induce UC, followed 7 days later by treatment with saline (blank control and model groups) or JWHQ Decoction by gavage (10 mL/k) for 7 consecutive days. After the treatment, the mice were euthanized and the colon length was measured and the histopathological changes were observed with HE staining. The expression levels of STAT3, NF-κB, and IL-6 in the colon tissues were detected with RT-qPCR and Western blotting.
Results: Compared with those in the blank control group, the colon length was significantly shortened and the pathological score of the colon tissue was significantly higher in all the other 5 groups (P < 0.05). Compared with those in the model group, the colon length was significantly longer and the pathological scores were obviously reduced in all the 4 treatment groups (P < 0.05). JWHQ Decoction at the high dose produced significantly better therapeutic effects than the positive drug in terms of the colon length (P < 0.05) and the colon histopathological score (P < 0.05); high-dose JWHQ Decoction also showed better effect than the other two doses (P < 0.05), whose effects were comparable (P > 0.05). The mouse models of UC showed significantly increased expression levels of STAT3, NF-κB, and IL-6 in the colon tissue (P < 0.01), which were obviously lowered by the positive drug and JWHQ Decoction (P < 0.01), especially at the high dose (P < 0.01). JWHQ Decoction at the moderate dose produced similar effects with the positive drug on STAT3, NF-kB and IL-6 levels (P > 0.05), and their effects were stronger than those of low-dose JWHQ Decoction (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: JWHQ Decoction can improve UC in mice possibly by down-regulating the expression of STAT3, NF-kB and IL-6 in colonic tissue to affect the STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6 pathway.
目的: 探讨加味黄芩汤对溃疡性结肠炎的治疗效果及对STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6通路的调控作用。
方法: 将48只小鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、阳性药物组(柳氮磺吡啶)、中药低剂量组、中药中剂量组、中药高剂量组,8只/组,按照3% DSS造模法对除空白组以外的5组小鼠进行溃疡性结肠炎造模,造模7 d后,空白组和模型组以生理盐水灌胃,药物治疗组以相应的药物灌胃,灌胃量均为10 ml/kg,共持续1周。治疗结束后,使用颈椎脱臼法处死小鼠,测量结肠长度,通过HE染色法观察各组小鼠结肠组织形态变化及结肠组织病理学评分变化,通过RT-qPCR法和Western blot法检测各组小鼠结肠组织STAT3、NF-kB、IL-6 mRNA及蛋白表达水平变化。
结果: 与空白组相比,模型组、阳性药物组及中药各剂量组小鼠结肠长度明显缩短(P < 0.05),结肠组织病理评分均明显升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,阳性药物组及中药各剂量组小鼠结肠长度明显延长(P < 0.05),结肠组织病理评分均明显降低(P < 0.05);与阳性药物组相比,中药高剂量组小鼠结肠长度明显延长(P < 0.05),结肠组织病理评分均明显降低(P < 0.05),中药中剂量组结肠长度及结肠组织病理评分均无明显差异(P > 0.05)、中药低剂量组结肠长度明显缩短(P < 0.05),结肠组织病理评分均明显增加(P < 0.05);与中药高剂量组相比,中药中、低剂量组小鼠结肠长度均明显缩短(P < 0.05),结肠组织病理评分均明显增加(P < 0.05);与中药中剂量组相比,中药低剂量组小鼠结肠长度均明显缩短(P < 0.05),结肠组织病理评分均明显增加(P < 0.05)。与空白组相比,模型组结肠组织STAT3、NF-kB、IL-6 mRNA及蛋白表达水平明显升高(P < 0.01),与模型组相比,阳性药物组及中药各剂量组结肠组织STAT3、NF-kB、IL-6 mRNA及蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.01),其中中药高剂量组结肠组织STAT3、NF-kB、IL-6 mRNA及蛋白表达水平明显低于阳性药物组及中药中、低剂量组(P < 0.05)。而中药中剂量组结肠组织STAT3、NF-kB、IL-6 mRNA及蛋白表达水平与阳性药物组无明显差异(P > 0.05),但明显低于中药低剂量组(P < 0.05)。
结论: 加味黄芩汤对溃疡性结肠炎具有一定的改善作用,其作用机制可能与通过影响STAT3/NF-kB/IL-6通路下调结肠组织STAT3、NF-kB、IL-6表达有关。
Keywords: Jiawei Huangqin decoction; STAT3; interleukin-6; nuclear factor-κB; ulcerative colitis.
Figures



References
-
- Guslandi M, Frego R, Viale E, et al. Distal ulcerative colitis refractory to rectal mesalamine: role of transdermal nicotine versus oral mesalamine. Can J Gastroenterol. 2002;16(5):293–6. doi: 10.1155/2002/307218. [Guslandi M, Frego R, Viale E, et al. Distal ulcerative colitis refractory to rectal mesalamine: role of transdermal nicotine versus oral mesalamine[J].Can J Gastroenterol, 2002, 16(5): 293-6.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Spagnuolo R, Dattilo V, D'antona L, et al. Deregulation of SGK1 in ulcerative colitis: a paradoxical relationship between immune cells and colonic epithelial cells. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018;24(9):e71–2. [Spagnuolo R, Dattilo V, D'antona L, et al. Deregulation of SGK1 in ulcerative colitis: a paradoxical relationship between immune cells and colonic epithelial cells[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2018, 24(9): e71-2.] - PubMed
-
- Martincuks A, Andryka K, Küster A, et al. Nuclear translocation of STAT3 and NF-κB are Independent of each other but NF-κB supports expression and activation of STAT3. Cell Signal. 2017;32(19):36–47. [Martincuks A, Andryka K, Küster A, et al. Nuclear translocation of STAT3 and NF-κB are Independent of each other but NF-κB supports expression and activation of STAT3[J]. Cell Signal, 2017, 32(19): 36-47.] - PubMed
-
- 范 文涛, 王 攀红, 王 倩. 马齿苋多糖对溃疡性结肠炎小鼠肠组织IL-6/ STAT3及NF-κB的影响. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGSL201803017.htm. 中国应用生理学杂志. 2018;34(3):73–7. [范文涛, 王攀红, 王倩.马齿苋多糖对溃疡性结肠炎小鼠肠组织IL-6/ STAT3及NF-κB的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志, 2018, 34(3): 73-7.]
-
-
Hao C, Duan WJ, Zhao HQ, et al. Comparison of the anti-inflammatory activity of Huangqin dispensing granules and Huangqin standard decoction[J].中国新药杂志, 2018, 27(11): 1309-14.
-
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
