The post-synaptic scaffolding protein tamalin regulates ligand-mediated trafficking of metabotropic glutamate receptors
- PMID: 32376687
- PMCID: PMC7307197
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011979
The post-synaptic scaffolding protein tamalin regulates ligand-mediated trafficking of metabotropic glutamate receptors
Abstract
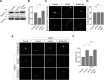
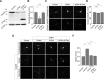
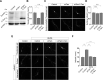
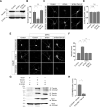
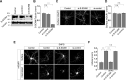
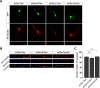
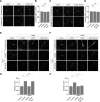
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) play important roles in various neuronal functions and have also been implicated in multiple neuropsychiatric disorders like fragile X syndrome, autism, and others. mGluR trafficking not only plays important roles in controlling the spatiotemporal localization of these receptors in the cell but also regulates the activity of these receptors. Despite this obvious significance, the cellular machineries that control the trafficking of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in the central nervous system have not been studied in detail. The post-synaptic scaffolding protein tamalin has been shown to interact with group I mGluRs and also with many other proteins involved in protein trafficking in neurons. Using a molecular replacement approach in mouse hippocampal neurons, we show here that tamalin plays a critical role in the ligand-dependent internalization of mGluR1 and mGluR5, members of the group I mGluR family. Specifically, knockdown of endogenous tamalin inhibited the ligand-dependent internalization of these two receptors. Both N-terminal and C-terminal regions of tamalin played critical roles in mGluR1 endocytosis. Furthermore, we found that tamalin regulates mGluR1 internalization by interacting with S-SCAM, a protein that has been implicated in vesicular trafficking. Finally, we demonstrate that tamalin plays a critical role in mGluR-mediated internalization of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors, a process believed to be the cellular correlate for mGluR-dependent synaptic plasticity. Taken together, these findings reveal a mechanistic role of tamalin in the trafficking of group I mGluRs and suggest its physiological implications in the brain.
Keywords: G-protein coupled receptor; S-SCAM; endocytosis; internalization; metabotropic glutamate receptors; neurotransmitter receptors; synaptic plasticity; tamalin; trafficking.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

