Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Protects Rats from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Accompanied with Biphasic Changes of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Signaling
- PMID: 32377532
- PMCID: PMC7183529
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3230490
Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Protects Rats from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Accompanied with Biphasic Changes of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Signaling
Abstract
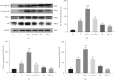
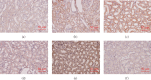
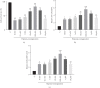
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of the most common and troublesome perioperative complications. Dexmedetomidine (DEX) is a potent α2-adrenoceptor (α2-AR) agonist with anti-inflammatory and renoprotective effects. In this study, a rat renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) model was induced. At 24 h after reperfusion, the IRI-induced damage and the renoprotection of DEX preconditioning were confirmed both biochemically and histologically. Changes in nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), as well as its downstream anti-inflammatory factor A20 and proinflammatory factor tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), were detected. Atipamezole, a nonselective antagonist, was then added 5 min before the administration of DEX to further analyze DEX's effects on NF-κB, and another anti-inflammatory medicine, methylprednisolone, was used in comparison with DEX, to further analyze DEX's effects on NF-κB. Different concentrations of DEX (0 nM, 0.1 nM, 1 nM, 10 nM, 100 nM, 1 μM, and 10 μM) were applied to preincubated human renal tubular epithelial cell line (HK-2) cells in vitro. After anoxia and reoxygenation, the MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) tetrazolium assay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were performed to evaluate the levels of NF-κB downstream anti-inflammatory cytokines. The results showed that, unlike methylprednisolone, DEX preconditioning led to a time-dependent biphasic change (first activation then inhibition) of NF-κB in the rat renal IRI models that were given 25 μg/kg i.p. It was accompanied by a similarly biphasic change of TNF-α and an early and persistent upregulation of A20. In vitro, DEX's cellular protection showed a concentration-dependent biphasic change which was protective within the range of 0 to 100 nM but became opposite when concentrations are greater than 1 μM. The changes in the A20 and NF-κB messenger RNA (mRNA) levels were consistent with the renoprotective ability of DEX. In other words, DEX preconditioning protected the rats from renal IRI via regulation biphasic change of NF-κB signaling.
Copyright © 2020 Naren Bao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Ameliorates Inflammation and Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Damage After Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Down-Regulation High Mobility Group Box 1-Toll-Like Receptor 4-Nuclear Factor κB Signaling Pathway.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019 Jan 15;44(2):E74-E81. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002772. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019. PMID: 29975331
-
Dexmedetomidine Protects Rat Liver against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Partly by the α2A-Adrenoceptor Subtype and the Mechanism Is Associated with the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 23;17(7):995. doi: 10.3390/ijms17070995. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27347929 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine preconditioning may attenuate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by down-regulating the HMGB1-TLR4-MyD88-NF-кB signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 21;12(2):e0172006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172006. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28222157 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine mitigation of renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury: comprehensive insights from cellular mechanisms to clinical application.Br J Anaesth. 2025 May;134(5):1350-1372. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2025.02.006. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Br J Anaesth. 2025. PMID: 40082177 Review.
-
Perioperative acute kidney injury: The renoprotective effect and mechanism of dexmedetomidine.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Feb 5;695:149402. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.149402. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38159412 Review.
Cited by
-
Organ-Protective Effects and the Underlying Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 May 9;2020:6136105. doi: 10.1155/2020/6136105. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32454792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexmedetomidine Protects Cortical Neurons from Propofol-Induced Apoptosis via Activation of Akt-IKK-NF-κB Signaling Pathway by α2A-adrenoceptor.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;196(8):4849-4861. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04768-4. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37979083
-
Intrarenal Arterial Transplantation of Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Adipose Stem-Cell-Derived Microvesicles Confers Further Therapeutic Potential to Attenuate Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through miR-122-5p/Erythropoietin/Apoptosis Axis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;11(9):1702. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091702. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139786 Free PMC article.
-
Carnosine alleviates diabetic nephropathy by targeting GNMT, a key enzyme mediating renal inflammation and fibrosis.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Dec 11;134(23):3175-3193. doi: 10.1042/CS20201207. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33241846 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative dexmedetomidine administration and acute kidney injury in patients undergoing unilateral partial nephrectomy: a retrospective study.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2409334. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2409334. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39351791 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

