Towards effective COVID‑19 vaccines: Updates, perspectives and challenges (Review)
- PMID: 32377694
- PMCID: PMC7255458
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4596
Towards effective COVID‑19 vaccines: Updates, perspectives and challenges (Review)
Abstract
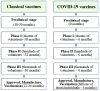
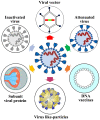
In the current context of the pandemic triggered by SARS-COV-2, the immunization of the population through vaccination is recognized as a public health priority. In the case of SARS‑COV‑2, the genetic sequencing was done quickly, in one month. Since then, worldwide research has focused on obtaining a vaccine. This has a major economic impact because new technological platforms and advanced genetic engineering procedures are required to obtain a COVID‑19 vaccine. The most difficult scientific challenge for this future vaccine obtained in the laboratory is the proof of clinical safety and efficacy. The biggest challenge of manufacturing is the construction and validation of production platforms capable of making the vaccine on a large scale.
Figures
References
-
- Kostoff RN. Georgia Institute of Technology; 2020. Combining Tactical and Strategic Treatments for COVID-19. http://hdl.handle.net/1853/62523 Accessed March 23 2020.
-
- Hashem MM, Abo-El-Sooud K, Abd-Elhakim YM, Badr YA, El-Metwally AE, Bahy-El-Dien A. The long-term oral exposure to titanium dioxide impaired immune functions and triggered cytotoxic and genotoxic impacts in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020;60:126473. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126473. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Torres M, Carranza C, Sarkar S, Gonzalez Y, Osornio Vargas A, Black K, Meng Q, Quintana-Belmares R, Hernandez M, Angeles Garcia JJF, et al. Urban airborne particle exposure impairs human lung and blood Mycobacterium tuberculosis immunity. Thorax. 2019;74:675–683. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-212529. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goumenou M, Sarigiannis D, Tsatsakis A, Anesti O, Docea AO, Petrakis D, Tsoukalas D, Kostoff R, Rakitskii V, Spandidos DA, et al. COVID-19 in Northern Italy: An integrative overview of factors possibly influencing the sharp increase of the outbreak (Review) Mol Med Rep. 2020;22:20–32. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous