Observational Study of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19
- PMID: 32379955
- PMCID: PMC7224609
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2012410
Observational Study of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19
Abstract
Background: Hydroxychloroquine has been widely administered to patients with Covid-19 without robust evidence supporting its use.
Methods: We examined the association between hydroxychloroquine use and intubation or death at a large medical center in New York City. Data were obtained regarding consecutive patients hospitalized with Covid-19, excluding those who were intubated, died, or discharged within 24 hours after presentation to the emergency department (study baseline). The primary end point was a composite of intubation or death in a time-to-event analysis. We compared outcomes in patients who received hydroxychloroquine with those in patients who did not, using a multivariable Cox model with inverse probability weighting according to the propensity score.
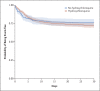
Results: Of 1446 consecutive patients, 70 patients were intubated, died, or discharged within 24 hours after presentation and were excluded from the analysis. Of the remaining 1376 patients, during a median follow-up of 22.5 days, 811 (58.9%) received hydroxychloroquine (600 mg twice on day 1, then 400 mg daily for a median of 5 days); 45.8% of the patients were treated within 24 hours after presentation to the emergency department, and 85.9% within 48 hours. Hydroxychloroquine-treated patients were more severely ill at baseline than those who did not receive hydroxychloroquine (median ratio of partial pressure of arterial oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen, 223 vs. 360). Overall, 346 patients (25.1%) had a primary end-point event (180 patients were intubated, of whom 66 subsequently died, and 166 died without intubation). In the main analysis, there was no significant association between hydroxychloroquine use and intubation or death (hazard ratio, 1.04, 95% confidence interval, 0.82 to 1.32). Results were similar in multiple sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions: In this observational study involving patients with Covid-19 who had been admitted to the hospital, hydroxychloroquine administration was not associated with either a greatly lowered or an increased risk of the composite end point of intubation or death. Randomized, controlled trials of hydroxychloroquine in patients with Covid-19 are needed. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health.).
Copyright © 2020 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Urgency of Care during the Covid-19 Pandemic - Learning as We Go.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 18;382(25):2461-2462. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2015903. Epub 2020 May 7. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32379956 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pour un retour à un développement rationnel des traitements.Rev Med Suisse. 2020 Jul 15;16(700):1388-1389. Rev Med Suisse. 2020. PMID: 32672019 French. No abstract available.
-
Renin-angiotensin system blockers and outcomes during hydroxychloroquine treatment in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 pneumonia.Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2020 Nov;73(11):964-966. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2020. PMID: 32792314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of Hydroxychloroquine on Antibody Responses to the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 4;11:1739. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01739. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849619 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Biot C, Daher W, Chavain N, et al. Design and synthesis of hydroxyferroquine derivatives with antimalarial and antiviral activities. J Med Chem 2006;49:2845-2849. - PubMed
-
- Fox RI. Mechanism of action of hydroxychloroquine as an antirheumatic drug. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1993;23:Suppl 1:82-91. - PubMed
-
- Wilson KC, Chotirmall SH, Bai C, Rello J. COVID-19: interim guidance on management pending empirical evidence. April 3, 2020. (https://www.thoracic.org/covid/covid-19-guidance.pdf).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical