CCNE1 Amplification as a Predictive Biomarker of Chemotherapy Resistance in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 32380689
- PMCID: PMC7277958
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10050279
CCNE1 Amplification as a Predictive Biomarker of Chemotherapy Resistance in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
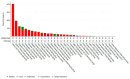
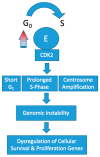
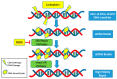
Ovarian cancer is the most-deadly gynecologic malignancy, with greater than 14,000 women expected to succumb to the disease this year in the United States alone. In the front-line setting, patients are treated with a platinum and taxane doublet. Although 40-60% of patients achieve complete clinical response to first-line chemotherapy, 25% are inherently platinum-resistant or refractory with a median overall survival of about one year. More than 80% of women afflicted with ovarian cancer will recur. Many attempts have been made to understand the mechanism of platinum and taxane based chemotherapy resistance. However, despite decades of research, few predictive markers of chemotherapy resistance have been identified. Here, we review the current understanding of one of the most common genetic alterations in epithelial ovarian cancer, CCNE1 (cyclin E1) amplification, and its role as a potential predictive marker of cytotoxic chemotherapy resistance. CCNE1 amplification has been identified as a primary oncogenic driver in a subset of high grade serous ovarian cancer that have an unmet clinical need. Understanding the interplay between cyclin E1 amplification and other common ovarian cancer genetic alterations provides the basis for chemotherapeutic resistance in CCNE1 amplified disease. Exploration of the effect of cyclin E1 amplification on the cellular machinery that causes dysregulated proliferation in cancer cells has allowed investigators to explore promising targeted therapies that provide the basis for emerging clinical trials.
Keywords: CCNE1 amplification; DNA damage response; chemotherapy resistance; cyclin E1; ovarian cancer; predictive biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fleming G., Seidman J., Yemelyanova A., Lengyel E. Chapter 23—Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. In: Chi D., Berchuck A., Dizon D., Yashar C., editors. Principles and Practice of Gynecologic Oncology. 7th ed. Wolters Kluwer; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2017. pp. 611–705.
-
- McGuire W.P., Hoskins W.J., Brady M.F., Kucera P.R., Partridge E.E., Look K.Y., Clarke-Pearson D.L., Davidson M. Cyclophosphamide and cisplatin compared with paclitaxel and cisplatin in patients with stage III and stage IV ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996;334:1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199601043340101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network Ovarian cancer: Including fallopian tube cancer and primary peritoneal cancer. NCCN Clin. Pract. Guid. Oncol. 2018;1:1–115.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

