Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Treatment for Severe COVID-19
- PMID: 32380908
- PMCID: PMC7310206
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2020.0080
Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Treatment for Severe COVID-19
Abstract
This prospective nonrandomized open-label cohort study addresses the safety and efficacy of exosomes (ExoFlo™) derived from allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as treatment for severe COVID-19. During April 2020, ExoFlo was provided to 24 SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction-positive patients at a single hospital center, all of whom met criteria for severe COVID-19 as well as moderate-to-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Patients received a single 15 mL intravenous dose of ExoFlo and were evaluated for both safety and efficacy from days 1 to 14 post-treatment. All safety endpoints were met with no adverse events observed within 72 h of ExoFlo administration. A survival rate of 83% was observed. In total, 17 of 24 (71%) patients recovered, 3 of 24 (13%) patients remained critically ill though stable, and 4 of 24 (16%) patients expired for reasons unrelated to the treatment. Overall, after one treatment, patients' clinical status and oxygenation improved with an average pressure of arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen ratio (PaO2/FiO2) increase of 192% (P < 0.001). Laboratory values revealed significant improvements in absolute neutrophil count [mean reduction 32% (P value <0.001)] and lymphopenia with average CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ lymphocyte counts increasing by 46% (P < 0.05), 45% (P < 0.05), and 46% (P < 0.001), respectively. Likewise, acute phase reactants declined, with mean C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer reduction of 77% (P < 0.001), 43% (P < 0.001), and 42% (P < 0.05), respectively. In conclusion, owing to its safety profile, capacity to restore oxygenation, downregulate cytokine storm, and reconstitute immunity, ExoFlo is a promising therapeutic candidate for severe COVID-19. Future randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are needed to determine ExoFlo therapeutic potential.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; MSC; SARS-CoV-2; bone marrow; exosome.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
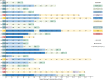

Comment in
-
Response to Lim et al. re: "Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Treatment for Severe COVID-19".Stem Cells Dev. 2020 Jul;29(14):879-881. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0095. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Stem Cells Dev. 2020. PMID: 32520639 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Re: "Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Treatment for Severe COVID-19" by Sengupta et al.Stem Cells Dev. 2020 Jul;29(14):877-878. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0089. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Stem Cells Dev. 2020. PMID: 32520641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Weiss Response to Sengupta et al. (DOI: 10.1089/scd.2020.0095).Stem Cells Dev. 2020 Dec;29(24):1533-1534. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0114. Stem Cells Dev. 2020. PMID: 33301389 No abstract available.
-
Lazo Response to Weiss et al. (Re: DOI: 10.1089/scd.2020.0114).Stem Cells Dev. 2021 Jan 1;30(1):1. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.29007.laz. Stem Cells Dev. 2021. PMID: 33404357 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gattinoni L, Coppola S, Cressoni M, Busana M and Chiumello D (2020). COVID-19 does not lead to a “Typical” acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. Advance online publication. Available at https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/abs/10.1164/rccm.202003-0817LE - PMC - PubMed
-
- CNARC report on COVID-19 in critical care. (2020). United Kingdom. Intensive Care National Audit Research Centre
-
- Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, Barnaby DP, Becker LB, Chelico JD, et al. (2020). Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. Advance online publication. 10.1001/jama.2020.6775 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

