Neurological Prognostication in Children After Cardiac Arrest
- PMID: 32381279
- PMCID: PMC7354677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2020.03.010
Neurological Prognostication in Children After Cardiac Arrest
Abstract
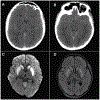
Early after pediatric cardiac arrest, families and care providers struggle with the uncertainty of long-term neurological prognosis. Cardiac arrest characteristics such as location, intra-arrest factors, and postarrest events have been associated with outcome. We paid particular attention to postarrest modalities that have been shown to predict neurological outcome. These modalities include neurological examination, somatosensory evoked potentials, electroencephalography, and neuroimaging. There is no one modality that accurately predicts neurological prognosis. Thus, a multimodal approach should be undertaken by both neurologists and intensivists to present a clear and consistent message to families. Methods used for the prediction of long-term neurological prognosis need to be specific enough to identify indivuals with a poor outcome. We review the evidence evaluating children with coma, each with various etiologies of cardiac arrest, outcome measures, and timing of follow-up.
Keywords: EEG; MRI; Outcome; Pediatric cardiac arrest; Prognostication; SEP.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

