Whole-slide image analysis of the tumor microenvironment identifies low B-cell content as a predictor of adverse outcome in patients with advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma treated with BEACOPP
- PMID: 32381573
- PMCID: PMC8168506
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2019.243287
Whole-slide image analysis of the tumor microenvironment identifies low B-cell content as a predictor of adverse outcome in patients with advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma treated with BEACOPP
Abstract
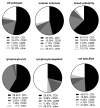
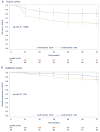
A subset of patients with advanced-stage classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (cHL) relapse or progress following standard treatment. Given their dismal prognosis, identifying this group of patients upfront represents an important medical need. While prior research has identified characteristics of the tumor microenvironment, which are associated with cHL outcomes, biomarkers that are developed and validated in this high-risk group are still missing. Here, we applied whole-slide image analysis (WSI), a quantitative, large-scale assessment of tumor composition that utilizes conventional histopathology slides. We conducted WSI on a study cohort with pre-treatment biopsies of 340 advanced-stage cHL patients enrolled in the HD12 and HD15 trials of the German Hodgkin Study Group (GHSG), and tested our results in in a validation cohort of 147 advanced-stage cHL patients within the GHSG HD18 trial. All patients were treated with BEACOPP-based regimens. By quantifying T cells, B cells, Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg-cells and macrophages with WSI, 80% of all cells in the tumor tissue were identified. Crucially, low B cell count was associated with significantly reduced progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), while T cell-, macrophage- and Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg-cell content was not associated with the risk of progression or relapse in the study cohort. We further validated low B cell content as a prognostic factor of PFS and OS in the validation cohort and demonstrate good inter-observer agreement of WSI. WSI may represent a key tool for risk stratification of advanced-stage cHL that can easily be added to the standard diagnostic histopathology work-up.
Figures


References
-
- Diehl V, Franklin J, Pfreundschuh M, et al. . Standard and increased-dose BEACOPP chemotherapy compared with COPPABVD for advanced Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(24):2386-2395. - PubMed
-
- Sjoberg J, Halthur C, Kristinsson SY, et al. . Progress in Hodgkin lymphoma: a population- based study on patients diagnosed in Sweden from 1973-2009. Blood. 2012; 119(4):990-996. - PubMed
-
- Goodman KA, Riedel E, Serrano V, et al. . Long-term effects of high-dose chemotherapy and radiation for relapsed and refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(32):5240-5247. - PubMed
-
- Eichenauer DA, Engert A, Andre M, et al. . Hodgkin's lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(Suppl 3):iii70-75. - PubMed
-
- Aoki T, Steidl C. Novel biomarker approaches in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer J. 2018;24(5):206-214. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

