Micro-Nano formulation of bile-gut delivery: rheological, stability and cell survival, basal and maximum respiration studies
- PMID: 32382021
- PMCID: PMC7205980
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-64355-z
Micro-Nano formulation of bile-gut delivery: rheological, stability and cell survival, basal and maximum respiration studies
Abstract
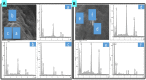
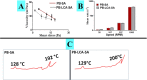
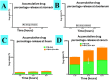
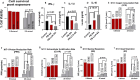
Probucol (PB) is a drug that exhibits significant hydrophobicity and substantial intra and inter individual variability in oral absorption, with a miniature bioavailability and complex three compartmental pharmacokinetic modelling due to its high lipid affinity, low stability and high octanol to water partition coefficient. Multiple attempts to formulate PB have not produced satisfactory stable matrices, drug-release profile or rheological flow properties for optimum manufacturing conditions, and with positive and none toxic biological effects. Lithocholic acid (LCA) has recently shown to optimise formulation and cell uptake of drugs. Hence, the aim of this study was to design new PB delivery system, using LCA, and examine its morphology, rheology, stability, and cellular effects. PB was formulated with LCA and sodium alginate (PB-LCA-SA) using various microencapsulation methodologies, and best formulation was investigated in vitro and ex vivo. Using our Ionic Gelation Vibrational Jet flow technology, PB-LCA-SA microcapsules showed good stability and significantly enhanced cell viability, cellular respiration, and reduced inflammation suggesting potential LCA applications in PB delivery and biological effects.
Conflict of interest statement
Al-Salami H. has been and is currently receiving funding from Beijing Nat-Med Biotechnology Co. Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of a tertiary bile acid, taurocholic acid, on the morphology and physical characteristics of microencapsulated probucol: potential applications in diabetes: a characterization study.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015 Oct;5(5):511-22. doi: 10.1007/s13346-015-0248-9. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 26242686
-
Novel chenodeoxycholic acid-sodium alginate matrix in the microencapsulation of the potential antidiabetic drug, probucol. An in vitro study.J Microencapsul. 2015;32(6):589-97. doi: 10.3109/02652048.2015.1065922. Epub 2015 Jul 20. J Microencapsul. 2015. PMID: 26190214
-
Multicompartmental, multilayered probucol microcapsules for diabetes mellitus: Formulation characterization and effects on production of insulin and inflammation in a pancreatic β-cell line.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016 Nov;44(7):1642-53. doi: 10.3109/21691401.2015.1069299. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26377035
-
Alginate-based drug oral targeting using bio-micro/nano encapsulation technologies.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Oct;17(10):1361-1376. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1789587. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32597249 Review.
-
Microencapsulation of Coenzyme Q10 and bile acids using ionic gelation vibrational jet flow technology for oral delivery.Ther Deliv. 2020 Dec;11(12):791-805. doi: 10.4155/tde-2020-0082. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Ther Deliv. 2020. PMID: 33225829 Review.
Cited by
-
Probucol Pharmacological and Bio-Nanotechnological Effects on Surgically Transplanted Graft Due to Powerful Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Fibrotic and Potential Bile Acid Modulatory Actions.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 20;13(8):1304. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081304. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452266 Free PMC article.
-
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Pharmacology in Biotechnology and Transplantable Pharmaceutical Applications for Tissue Delivery: An Acute Preclinical Study.Cells. 2021 Sep 16;10(9):2437. doi: 10.3390/cells10092437. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572086 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Assessments of Bio-Tissue Engineering and Viable Cell Delivery Matrices Using Bile Acid-Based Pharmacological Biotechnologies.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jul 19;11(7):1861. doi: 10.3390/nano11071861. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34361247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced Bilosomal Properties Resulted in Optimum Pharmacological Effects by Increased Acidification Pathways.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 31;13(8):1184. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081184. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452145 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Recent Advancement on Age-Related Hearing Loss: The Applications of Nanotechnology, Drug Pharmacology, and Biotechnology.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 8;13(7):1041. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13071041. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34371732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Humberstone AJ, Charman WN. Lipid-based vehicles for the oral delivery of poorly water soluble drugs. Advanced drug delivery reviews. 1997;25:103–128. doi: 10.1016/S0169-409X(96)00494-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

