PKCθ-JunB axis via upregulation of VEGFR3 expression mediates hypoxia-induced pathological retinal neovascularization
- PMID: 32382040
- PMCID: PMC7206019
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-2522-0
PKCθ-JunB axis via upregulation of VEGFR3 expression mediates hypoxia-induced pathological retinal neovascularization
Abstract
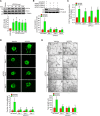
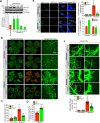
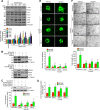
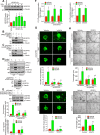
Pathological retinal neovascularization is the most common cause of vision loss. PKCθ has been shown to play a role in type 2 diabetes, which is linked to retinal neovascularization. Based on these clues, we have studied the role of PKCθ and its downstream target genes JunB and VEGFR3 in retinal neovascularization using global and tissue-specific knockout mouse models along with molecular biological approaches. Here, we show that vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) induces PKCθ phosphorylation in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMVECs) and downregulation of its levels attenuates VEGFA-induced HRMVECs migration, sprouting and tube formation. Furthermore, the whole body deletion of PKCθ or EC-specific deletion of its target gene JunB inhibited hypoxia-induced retinal EC proliferation, tip cell formation and neovascularization. VEGFA also induced VEGFR3 expression via JunB downstream to PKCθ in the regulation of HRMVEC migration, sprouting, and tube formation in vitro and OIR-induced retinal EC proliferation, tip cell formation and neovascularization in vivo. In addition, VEGFA-induced VEGFR3 expression requires VEGFR2 activation upstream to PKCθ-JunB axis both in vitro and in vivo. Depletion of VEGFR2 or VEGFR3 levels attenuated VEGFA-induced HRMVEC migration, sprouting and tube formation in vitro and retinal neovascularization in vivo and it appears that these events were dependent on STAT3 activation. Furthermore, the observations using soluble VEGFR3 indicate that VEGFR3 mediates its effects on retinal neovascularization in a ligand dependent and independent manner downstream to VEGFR2. Together, these observations suggest that PKCθ-dependent JunB-mediated VEGFR3 expression targeting STAT3 activation is required for VEGFA/VEGFR2-induced retinal neovascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 via enhancing signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-dependent cJun expression mediates retinal neovascularization.Sci Rep. 2016 May 23;6:26480. doi: 10.1038/srep26480. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27210483 Free PMC article.
-
A new role for cofilin in retinal neovascularization.J Cell Sci. 2016 Mar 15;129(6):1234-49. doi: 10.1242/jcs.179382. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 26857814 Free PMC article.
-
VEGFR3 Modulates Vascular Permeability by Controlling VEGF/VEGFR2 Signaling.Circ Res. 2017 Apr 28;120(9):1414-1425. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310477. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28298294 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Function of PKCtheta in Cancer.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 5;11(2):221. doi: 10.3390/biom11020221. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33562506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key transcriptional regulators of early vascular development.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Jul;31(7):1469-75. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.221168. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21677289 Review.
Cited by
-
Salidroside Prevents Hypoxia-Induced Human Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cell Damage Via miR-138/ROBO4 Axis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jul 1;62(9):25. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.9.25. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34269814 Free PMC article.
-
JunB condensation attenuates vascular endothelial damage under hyperglycemic condition.J Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Apr 10;15(12):mjad072. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjad072. J Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38140943 Free PMC article.
-
JunB: a paradigm for Jun family in immune response and cancer.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Sep 4;13:1222265. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1222265. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37731821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Role of Prereplication Complex Component Cell Division Cycle 6 in Retinal Neovascularization.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022 Apr;42(4):407-427. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.317182. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022. PMID: 35236105 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-Regulated Protein 78, via Releasing β-Catenin from Adherens Junctions, Facilitates Its Interaction with STAT3 in Mediating Retinal Neovascularization.Am J Pathol. 2024 Dec;194(12):2356-2381. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2024.08.005. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Am J Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39222910
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

