Clinical utility of the exosome based ExoDx Prostate(IntelliScore) EPI test in men presenting for initial Biopsy with a PSA 2-10 ng/mL
- PMID: 32382078
- PMCID: PMC7655505
- DOI: 10.1038/s41391-020-0237-z
Clinical utility of the exosome based ExoDx Prostate(IntelliScore) EPI test in men presenting for initial Biopsy with a PSA 2-10 ng/mL
Abstract
Background: The ExoDx Prostate(IntelliScore) (EPI) test is a non-invasive risk assessment tool for detection of high-grade prostate cancer (HGPC) that informs whether to proceed with prostate biopsy. We sought to assess the impact of EPI on the decision to biopsy in a real-world clinical setting.
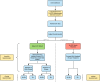
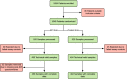
Methods: We conducted a prospective, randomized, blinded, two-armed clinical utility study that enrolled 1094 patients with 72 urologists from 24 urology practices. Patients were considered for prostate biopsy at enrollment based on standard clinical criteria. All patients had an EPI test; however, patients were randomized into EPI vs. control arms where only the EPI arm received results for their biopsy decision.
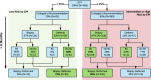
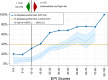
Results: In the EPI arm (N = 458), 93 patients received negative EPI scores of which 63% were recommended to defer biopsy by the urologist and 74% ultimately deferred. In contrast, 87% of patients with positive EPI scores were recommended to undergo biopsy with a 72% compliance rate to the urologist's recommendation. This led to detection of 30% more HGPC compared to the control arm, and we estimate that 49% fewer HGPC were missed due to deferrals compared to standard of care (SOC). Overall, 68% of urologists reported that the EPI test influenced their biopsy decision. The primary reason not to comply with EPI results was rising PSA.
Conclusion: To our knowledge this is the first report on a PC biomarker utility study with a blinded control arm. The study demonstrates that the EPI test influences the overall decision to defer or proceed with a biopsy and improves patient stratification.
Conflict of interest statement
PT, VT, MN and JS are employees of Bio-techne. TM and MJD are consultants for Bio-Techne. ARF: personal relationship with PCAN EIC. Editor recused himself and was not involved in the processing of this manuscript or the editorial decision-making.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Prospective Adaptive Utility Trial to Validate Performance of a Novel Urine Exosome Gene Expression Assay to Predict High-grade Prostate Cancer in Patients with Prostate-specific Antigen 2-10ng/ml at Initial Biopsy.Eur Urol. 2018 Dec;74(6):731-738. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 30237023 Clinical Trial.
-
ExoDx prostate test as a predictor of outcomes of high-grade prostate cancer - an interim analysis.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023 Sep;26(3):596-601. doi: 10.1038/s41391-023-00675-1. Epub 2023 May 16. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023. PMID: 37193776 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Predicting high-grade prostate cancer at initial biopsy: clinical performance of the ExoDx (EPI) Prostate Intelliscore test in three independent prospective studies.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022 Feb;25(2):296-301. doi: 10.1038/s41391-021-00456-8. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022. PMID: 34593984 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of serum, urine, and tissue-based prostate cancer biomarkers.Curr Opin Urol. 2025 Jul 1;35(4):412-417. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000001293. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Curr Opin Urol. 2025. PMID: 40292531 Review.
-
Evaluation of blood and urine based biomarkers for detection of clinically-significant prostate cancer.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025 Mar;28(1):45-55. doi: 10.1038/s41391-024-00840-0. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025. PMID: 38858447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of potential RNA biomarkers for prostate cancer diagnosis and monitoring in plasma and urinary extracellular vesicles.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 30;10:1279854. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1279854. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38099195 Free PMC article.
-
The differential presence of human polyomaviruses, JCPyV and BKPyV, in prostate cancer and benign prostate hypertrophy tissues.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 24;21(1):1141. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08862-w. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34689739 Free PMC article.
-
[Prostate cancer screening-current overview].Radiologie (Heidelb). 2024 Jun;64(6):479-487. doi: 10.1007/s00117-024-01312-1. Epub 2024 May 14. Radiologie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38743100 Review. German.
-
Methods for Extracellular Vesicle Isolation: Relevance for Encapsulated miRNAs in Disease Diagnosis and Treatment.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 12;16(3):330. doi: 10.3390/genes16030330. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular RNAs as potential biomarkers for cancer.J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2020;6:32. doi: 10.20517/2394-4722.2020.71. Epub 2020 Sep 17. J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2020. PMID: 33490601 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

