Modeling shield immunity to reduce COVID-19 epidemic spread
- PMID: 32382154
- PMCID: PMC8272982
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-020-0895-3
Modeling shield immunity to reduce COVID-19 epidemic spread
Abstract
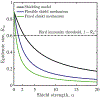
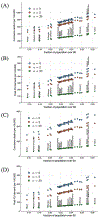
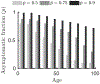
The COVID-19 pandemic has precipitated a global crisis, with more than 1,430,000 confirmed cases and more than 85,000 confirmed deaths globally as of 9 April 20201-4. Mitigation and suppression of new infections have emerged as the two predominant public health control strategies5. Both strategies focus on reducing new infections by limiting human-to-human interactions, which could be both socially and economically unsustainable in the long term. We have developed and analyzed an epidemiological intervention model that leverages serological tests6,7 to identify and deploy recovered individuals8 as focal points for sustaining safer interactions via interaction substitution, developing what we term 'shield immunity' at the population scale. The objective of a shield immunity strategy is to help to sustain the interactions necessary for the functioning of essential goods and services9 while reducing the probability of transmission. Our shield immunity approach could substantively reduce the length and reduce the overall burden of the current outbreak, and can work synergistically with social distancing. The present model highlights the value of serological testing as part of intervention strategies, in addition to its well-recognized roles in estimating prevalence10,11 and in the potential development of plasma-based therapies12-15.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




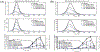
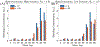

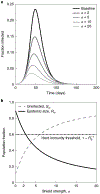
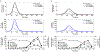
Update of
-
Intervention Serology and Interaction Substitution: Modeling the Role of 'Shield Immunity' in Reducing COVID-19 Epidemic Spread.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Apr 3:2020.04.01.20049767. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.01.20049767. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Med. 2020 Jun;26(6):849-854. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0895-3. PMID: 32511605 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Protecting the population with immune individuals.Nat Med. 2020 Jun;26(6):823-824. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0896-2. Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 32382153 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report 70 (2020); https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2...
-
- Ferguson N et al. Impact of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs) to Reduce COVID19 Mortality and Healthcare Demand (Imperial College, 2020); https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/medicine/sph/ide/gida-... - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI146592/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 329108/Simons Foundation/International
- 1829636/National Science Foundation (NSF)/International
- 1R01AI46592-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- 1806606/National Science Foundation/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

