Chloroquine Inhibits the Release of Inflammatory Cytokines by Human Lung Explants
- PMID: 32382733
- PMCID: PMC7454417
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa546
Chloroquine Inhibits the Release of Inflammatory Cytokines by Human Lung Explants
Abstract
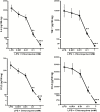
On human lung parenchymal explants, chloroquine concentration clinically achievable in the lung (100 µM) inhibited the lipopolysaccharide-induced release of TNF-ɑ (by 76%), IL-6 (by 68%), CCL2 (by 72%), and CCL3 (by 67%). Besides its antiviral activity, chloroquine might also mitigate the cytokine storm associated with severe pneumonia caused by coronaviruses.
Keywords: chemokine; chloroquine; interleukin-6; lung explant; tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Gao J, Tian Z, Yang X. Breakthrough: chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci Trends 2020; 14:72–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

