Magnetic Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents
- PMID: 32382832
- PMCID: PMC8203530
- DOI: 10.1007/s41061-020-00302-w
Magnetic Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Magnetic Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021 Jun 14;379(4):30. doi: 10.1007/s41061-021-00340-y. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021. PMID: 34128112 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
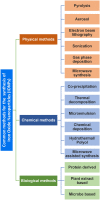
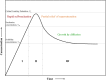
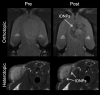
Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) have emerged as a promising alternative to conventional contrast agents (CAs) for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). They have been extensively investigated as CAs due to their high biocompatibility and excellent magnetic properties. Furthermore, the ease of functionalization of their surfaces with different types of ligands (antibodies, peptides, sugars, etc.) opens up the possibility of carrying out molecular MRI. Thus, IONPs functionalized with epithelial growth factor receptor antibodies, short peptides, like RGD, or aptamers, among others, have been proposed for the diagnosis of various types of cancer, including breast, stomach, colon, kidney, liver or brain cancer. In addition to cancer diagnosis, different types of IONPs have been developed for other applications, such as the detection of brain inflammation or the early diagnosis of thrombosis. This review addresses key aspects in the development of IONPs for MRI applications, namely, synthesis of the inorganic core, functionalization processes to make IONPs biocompatible and also to target them to specific tissues or cells, and finally in vivo studies in animal models, with special emphasis on tumor models.
Keywords: Cancer; Diagnosis; Iron oxide nanoparticles; Magnetic nanoparticles; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures



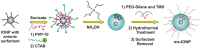
References
-
- García-Martín ML, López-Larrubia P. Preclinical MRI: methods and protocols, vol 1718. Methods in molecular biology. New York: Springer; 2018.
-
- Leong HS, Butler KS, Brinker CJ, Azzawi M, Conlan S, Dufés C, Owen A, Rannard S, Scott C, Chen C, Dobrovolskaia MA, Kozlov SV, Prina-Mello A, Schmid R, Wick P, Caputo F, Boisseau P, Crist RM, McNeil SE, Fadeel B, Tran L, Hansen SF, Hartmann NB, Clausen LPW, Skjolding LM, Baun A, Ågerstrand M, Gu Z, Lamprou DA, Hoskins C, Huang L, Song W, Cao H, Liu X, Jandt KD, Jiang W, Kim BYS, Wheeler KE, Chetwynd AJ, Lynch I, Moghimi SM, Nel A, Xia T, Weiss PS, Sarmento B, das Neves J, Santos HA, Santos L, Mitragotri S, Little S, Peer D, Amiji MM, Alonso MJ, Petri-Fink A, Balog S, Lee A, Drasler B, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Wilhelm S, Acar H, Harrison RG, Mao C, Mukherjee P, Ramesh R, McNally LR, Busatto S, Wolfram J, Bergese P, Ferrari M, Fang RH, Zhang L, Zheng J, Peng C, Du B, Yu M, Charron DM, Zheng G, Pastore C. On the issue of transparency and reproducibility in nanomedicine. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019;14(7):629–635. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0496-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhi D, Yang T, Yang J, Fu S, Zhang S (2020) Targeting strategies for superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Acta Biomater 102:13–34. 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.11.027 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
