APPA (apocynin and paeonol) modulates pathological aspects of human neutrophil function, without supressing antimicrobial ability, and inhibits TNFα expression and signalling
- PMID: 32383062
- PMCID: PMC7525285
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-020-00715-5
APPA (apocynin and paeonol) modulates pathological aspects of human neutrophil function, without supressing antimicrobial ability, and inhibits TNFα expression and signalling
Abstract
Neutrophils are key players in the pathophysiological process underlying inflammatory conditions not only by release of tissue-damaging cytotoxic enzymes, reactive oxygen species (ROS) but also by secretion of important immunomodulatory chemokines and cytokines. Here, we report the effects of the novel agent APPA, undergoing formal clinical development for treatment of osteoarthritis, and its constituent components, apocynin (AP) and paeonol (PA) on a number of neutrophil functions, including effects on TNFα- expression and signalling. Neutrophils were treated with APPA (10-1000 µg/mL) prior to the measurement of cell functions, including ROS production, chemotaxis, apoptosis and surface receptor expression. Expression levels of several key genes and proteins were measured after incubation with APPA and the chromatin re-modelling agent, R848. APPA did not significantly affect phagocytosis, bacterial killing or expression of surface receptors, while chemotactic migration was affected only at the highest concentrations. However, APPA down-regulated neutrophil degranulation and ROS levels, and decreased the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. APPA also decreased cytokine-stimulated gene expression, inhibiting both TNFα- and GM-CSF-induced cell signalling. APPA was as effective as infliximab in down-regulating chemokine and IL-6 expression following incubation with R848. Whilst APPA does not interfere with neutrophil host defence against infections, it does inhibit neutrophil degranulation, and cytokine-driven signalling pathways (e.g. autocrine signalling and NF-κB activation), processes that are associated with inflammation. These observations may explain the mechanisms by which APPA exerts anti-inflammatory effects and suggests a potential therapeutic role in inflammatory diseases in which neutrophils and TNFα signalling are important in pathology, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Keywords: APPA; Apocynin; NFκB; Neutrophil; Paeonol; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
NHS Health Research Authority (Inflammatory Signalling Pathways; Ref 11/NW/0206: IRAS project ID 75388). The authors declare that there were no conflicts of interest.
Figures
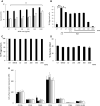
 ) or presence of cytokines known to regulate neutrophil apoptosis. Following 10-min pre-incubation with APPA, the following additions were made: GM-CSF (5 ng/mL,
) or presence of cytokines known to regulate neutrophil apoptosis. Following 10-min pre-incubation with APPA, the following additions were made: GM-CSF (5 ng/mL,  ) or TNFα (10 ng/mL,
) or TNFα (10 ng/mL,  ) and incubation was continued for a further 20 h (n = 7). In b neutrophils (106) from healthy controls were incubated in the absence (UT) or presence of APPA (10–1000 µg/mL) for 10 min, then migration towards fMLP (10−8 M) or IL-8 (100 ng/mL) was measured after a 90-min incubation period. Untreated neutrophils migrating towards fMLP (10−8 M) and IL-8 (100 ng/mL) are shown as positive controls (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.05). Values shown are means (± SEM, n = 4). In c and d, neutrophils were pre-incubated for 10 min with the indicated concentration of APPA (or DMSO vehicle control). In c, they were then incubated with a 10:1 ratio of PI-stained, heat-killed serum-opsonised S. aureus and phagocytosis was determined by flow cytometery. Values shown are mean MFI values (normalised to untreated control values of 100%), ± SD (n = 3). In d, neutrophils subsequently incubated with a 10:1 ratio of live, serum-opsonised S.aureus and after 1-h incubation, bacterial viability was determined by plate counting. Values shown are mean values ± SD (n = 3). In e, neutrophils were isolated from healthy controls and expression of cell surface receptors was measured on freshly isolated cells by flow cytometry. These levels of expression were compared with those on neutrophils pre-incubated with APPA (100 µg/mL) and stimulated for 1 h with either GM-CSF (5 ng/mL) or TNFα (10 ng/mL), as follows:
) and incubation was continued for a further 20 h (n = 7). In b neutrophils (106) from healthy controls were incubated in the absence (UT) or presence of APPA (10–1000 µg/mL) for 10 min, then migration towards fMLP (10−8 M) or IL-8 (100 ng/mL) was measured after a 90-min incubation period. Untreated neutrophils migrating towards fMLP (10−8 M) and IL-8 (100 ng/mL) are shown as positive controls (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.05). Values shown are means (± SEM, n = 4). In c and d, neutrophils were pre-incubated for 10 min with the indicated concentration of APPA (or DMSO vehicle control). In c, they were then incubated with a 10:1 ratio of PI-stained, heat-killed serum-opsonised S. aureus and phagocytosis was determined by flow cytometery. Values shown are mean MFI values (normalised to untreated control values of 100%), ± SD (n = 3). In d, neutrophils subsequently incubated with a 10:1 ratio of live, serum-opsonised S.aureus and after 1-h incubation, bacterial viability was determined by plate counting. Values shown are mean values ± SD (n = 3). In e, neutrophils were isolated from healthy controls and expression of cell surface receptors was measured on freshly isolated cells by flow cytometry. These levels of expression were compared with those on neutrophils pre-incubated with APPA (100 µg/mL) and stimulated for 1 h with either GM-CSF (5 ng/mL) or TNFα (10 ng/mL), as follows:  No additions;
No additions;  TNFα only;
TNFα only;  GM-CSF only;
GM-CSF only;  APPA only;
APPA only;  TNFα + APPA;
TNFα + APPA;  GM-CSF + APPA. Levels of CD11b, CD18, CD16, CD32, CD64 and CXCR1 (IL-8R) were measured. Inset shows effects of APPA with and without GM-CSF or TNFα on CD62L expression levels. There was no significant difference in surface marker expression following treatment with APPA. Values shown are means ± SD (n = 3)
GM-CSF + APPA. Levels of CD11b, CD18, CD16, CD32, CD64 and CXCR1 (IL-8R) were measured. Inset shows effects of APPA with and without GM-CSF or TNFα on CD62L expression levels. There was no significant difference in surface marker expression following treatment with APPA. Values shown are means ± SD (n = 3)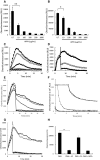
 ) untreated controls, while
) untreated controls, while  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , show APPA concentrations of 10, 10, 200, 500 and 1000 µg/mL, respectively. In D PMA-induced respiratory burst activity was stimulated (
, show APPA concentrations of 10, 10, 200, 500 and 1000 µg/mL, respectively. In D PMA-induced respiratory burst activity was stimulated ( ) and after 5-min incubation, APPA (at 10 µg/mL,
) and after 5-min incubation, APPA (at 10 µg/mL,  and 100 µg/mL:
and 100 µg/mL:  ) was added as indicated by the arrow. In e PMA was used to stimulate ROS production by neutrophils. As indicated by the arrow, the following additions were injected into the cell suspension:
) was added as indicated by the arrow. In e PMA was used to stimulate ROS production by neutrophils. As indicated by the arrow, the following additions were injected into the cell suspension:  , no additions;
, no additions;  , catalase (2U/mL);
, catalase (2U/mL);  , superoxide dismutase (40 µg/mL);
, superoxide dismutase (40 µg/mL);  , sodium azide (1 mM);
, sodium azide (1 mM);  , APPA (100 µg/mL). In f APPA (10–1000 µg/mL) or DMSO (as solvent control) were added to a cell-free luminol system utilizing hydrogen peroxide, as follows:
, APPA (100 µg/mL). In f APPA (10–1000 µg/mL) or DMSO (as solvent control) were added to a cell-free luminol system utilizing hydrogen peroxide, as follows:  , no additions;
, no additions;  , DMSO;
, DMSO;  , 10 µg/mL APPA;
, 10 µg/mL APPA;  , 100 µg/mL APPA;
, 100 µg/mL APPA;  , 200 µg/mL APPA;
, 200 µg/mL APPA;  , 500 µg/mL APPA. representative result of 3 separate experiments. In g, Neutrophils were stimulated with with PMA (
, 500 µg/mL APPA. representative result of 3 separate experiments. In g, Neutrophils were stimulated with with PMA ( ) and after 5-min incubation APPA (100 µg/mL,
) and after 5-min incubation APPA (100 µg/mL,  ), AP (22 µg/mL,
), AP (22 µg/mL,  ) or PA (78 µg/mL,
) or PA (78 µg/mL,  ) added, as indicated by the arrow. h Shows replicate data of total chemiluminescence from g, **p value < 0.01, n = 11
) added, as indicated by the arrow. h Shows replicate data of total chemiluminescence from g, **p value < 0.01, n = 11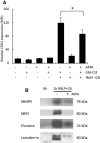
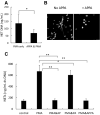
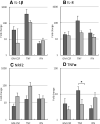
 ) or presence (
) or presence ( ) of APPA (100 µg/mL) for 10 min. APPA-treated neutrophils were then stimulated with GM-CSF, IFNγ or TNFα for 1 h. qPCR was used to quantify transcript levels of IL-1β (a), IL-8 (b), NRF2 (c) and TNFα (d). Values shown are mean (± SEM), n = 6, *p = 0.012
) of APPA (100 µg/mL) for 10 min. APPA-treated neutrophils were then stimulated with GM-CSF, IFNγ or TNFα for 1 h. qPCR was used to quantify transcript levels of IL-1β (a), IL-8 (b), NRF2 (c) and TNFα (d). Values shown are mean (± SEM), n = 6, *p = 0.012
References
-
- Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:280–288. - PubMed
-
- Boots AW, Gerloff K, Bartholome R, et al. Neutrophils augment LPS-mediated pro-inflammatory signaling in human lung epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1823:1151–1162. - PubMed
-
- Carmona-Rivera C, Kaplan MJ. Induction and Quantification of NETosis. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2016;115:14 41 1–14 41 14. - PubMed
-
- Cassatella MA. The production of cytokines by polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Immunol Today. 1995;16:21–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
