Beneficial effects of benfotiamine, a NADPH oxidase inhibitor, in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats
- PMID: 32384080
- PMCID: PMC7209119
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232413
Beneficial effects of benfotiamine, a NADPH oxidase inhibitor, in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats
Abstract
Background: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) remains the most common cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The present study was directed to investigate the beneficial effects of benfotiamine pre- and post-treatments in isoproterenol (ISO)-induced MI in rats.
Methods: Myocardial heart damage was induced by subcutaneous injection of ISO (150 mg/kg) once daily for two consecutive days. Benfotiamine (100 mg/kg/day) was given orally for two weeks before or after ISO treatment.
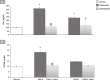
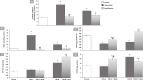
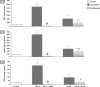
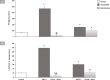
Results: ISO administration revealed significant changes in electrocardiographic recordings, elevation of levels of cardiac enzymes; creatinine kinase (CK-MB) and troponin-I (cTn-I), and perturbation of markers of oxidative stress; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase, malondialdehyde (MDA), reduced glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and markers of inflammation; protein kinase C (PKC), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). The apoptotic markers (caspase-8 and p53) were also significantly elevated in ISO groups in addition to histological alterations. Groups treated with benfotiamine pre- and post-ISO administration showed significantly decreased cardiac enzymes levels and improved oxidative stress, inflammatory and apoptotic markers compared to the ISO groups.
Conclusion: The current study highlights the potential role of benfotiamine as a promising agent for prophylactic and therapeutic interventions in myocardial damage in several cardiovascular disorders via NADPH oxidase inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
NO authors have competing interests.
Figures
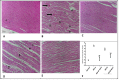
References
-
- Siddiqui MA, Ahmad U, Khan AA, Ahmad M, Badruddeen, Khalid M, et al. Isoprenaline: a Tool for Inducing Myocardial Infarction in Experimental Animals. Int J Pharm. 2016;6(2):138–44.
-
- Kloner RA. New Observations Regarding Post-Ischemia/Reperfusion Myocardial Swelling *. J Am Coll Cardiol [Internet]. 2015. February 3 [cited 2018 Aug 28];65(4):324–6. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25461691 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.11.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kiran Kumar G, Kala Kumar B, Boobalan G, Satish Kumar CSV, Gopala Reddy A. Cardioprotective potential of Lathyrus sativus against experimental myocardial infarction due to isoproterenol in rats. Indian Vet J. 2017;94(5):41–3.
-
- Ong S-B, Hernández-Reséndiz S, Crespo-Avilan GE, Mukhametshina RT, Kwek X-Y, Cabrera-Fuentes HA, et al. Inflammation following acute myocardial infarction: Multiple players, dynamic roles, and novel therapeutic opportunities. Pharmacol Ther [Internet]. 2018. [cited 2019 May 23];186:73–87. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29330085 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu Q, Dalic A, Fang L, Kiriazis H, Ritchie RH, Sim K, et al. Myocardial oxidative stress contributes to transgenic β₂-adrenoceptor activation-induced cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Br J Pharmacol [Internet]. 2011. March [cited 2019 May 23];162(5):1012–28. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20955367 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01043.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

