Extracorporeal shockwave therapy combined with alginate dressing for treatment of sacroiliac decubital necrosis in older adults: A case report
- PMID: 32384429
- PMCID: PMC7220157
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019849
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy combined with alginate dressing for treatment of sacroiliac decubital necrosis in older adults: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Pressure sores are major clinical problems with limited treatment options.
Patient concern: A 62-year-old man, admitted with unresponsive, indifferent mood, and malnutrition. A noval-shaped skin lesion deeping into the fascia was found in the sacrococcygeal region.
Diagnosis: The patient was diagnosed with delayed carbon monoxide poisoning encephalopathy and stage IV sacrococcygeal pressure sores.
Intervention: The patient received neurologic rehabilitation therapy and simple debridement dressing care followed by extracorporeal shockwave therapy.
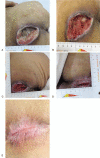
Outcomes: The scores for the pressure ulcer healing scale were 17 points, 13 points, 9 points, and 5 points, respectively, before treatment and at the 4-, 8-, and 12-week follow-ups. At 2 weeks after discharging the total pressure ulcer healing scale score was 0, which signifies that the sacroiliac decubital necrosis healed without adverse reactions and side effects.
Lessons: This study presents a therapeutic solution for treating older adults with pressure ulcers by using extracorporeal shockwave with alginate dressing, which proved effective and safe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of modified double negative-pressure wound therapy combined with debridement and tension-reduced suture in treatment of patients with stage 4 pressure sores and infection in sacrococcygeal region and its surrounding area].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 20;36(7):540-546. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200304-00118. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32842400 Chinese.
-
[Treatment of chronic wounds with an alginate dressing containing calcium zinc and manganese].Fortschr Med Orig. 2003;121(1):19-26. Fortschr Med Orig. 2003. PMID: 15117065 Clinical Trial. German.
-
[Pure calcium-sodium alginate dressing. Multicenter evaluation of chronic cutaneous lesions].Rev Enferm. 1997 Sep;20(229):23-30. Rev Enferm. 1997. PMID: 9385189 Clinical Trial. Spanish.
-
Wound care in venous ulcers.Phlebology. 2013 Mar;28 Suppl 1:79-85. doi: 10.1177/0268355513477015. Phlebology. 2013. PMID: 23482540 Review.
-
[Wound care with modern dressing materials].MMW Fortschr Med. 2009 Mar 5;151(10):29-32. MMW Fortschr Med. 2009. PMID: 19472664 Review. German. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Is Shock Wave Application Effective on Various Chronic Wounds in the Geriatric Population? Preliminary Clinical Study.Clin Interv Aging. 2024 Apr 30;19:665-679. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S448298. eCollection 2024. Clin Interv Aging. 2024. PMID: 38706636 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Jugun K, Richard JC, Lipsky BA, et al. Factors associated with treatment failure of infected pressure sores. Ann Surg 2016;264:399–403. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Zhuang YH, Xue L, et al. A composite gluteofemoral flap for reconstruction of large pressure sores over the sacrococcygeal region. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2015;68:1733–42. - PubMed
-
- Vorobiev A, Vorobiev P, Krasnova L. Telemedicine consultation in the differential diagnosis simple contact dermatitis due to incontinence and pressure sores in immobilized patients with urinary incontinence - clinical and economic analysis. Value Health 2015;18:346. - PubMed
-
- Choi EP, Chin WY, Wan EY, et al. Evaluation of the internal and external responsiveness of the pressure ulcer scale for healing (PUSH) tool for assessing acute and chronic wounds. J Adv Nurs 2016;72:1134–43. - PubMed
-
- Breslow RA, Hallfrisch J, Goldberg AP. Malnutrition in tube fed nursing home patients with pressure sores. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 1991;15:663–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical