Analysis of genes associated with prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma based on GEO and TCGA databases
- PMID: 32384511
- PMCID: PMC7220259
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020183
Analysis of genes associated with prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma based on GEO and TCGA databases
Abstract
Backgrounds: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is one of the most common malignancies, and is a serious threat to human health. The aim of the present study was to assess potential biomarkers for the prognosis of LUAD through the analysis of gene expression microarrays.
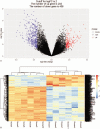
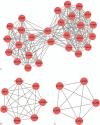
Methods: The gene expression data for GSE118370 was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between normal lung and LUAD samples were screened using the R language. The DAVID database was used to analyze the functions and pathways of DEGs. The STRING database was used to the map protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, and these were visualized with the Cytoscape software. Finally, the prognostic analysis of the hub gene in the PPI network was performed using the Kaplan-Meier tool.
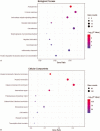
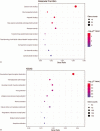
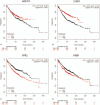
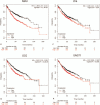
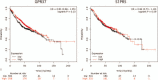
Results: A total of 406 downregulated and 203 upregulated DEGs were identified. The GO analysis results revealed that downregulated DEGs were significantly enriched in angiogenesis, calcium ion binding and cell adhesion. The upregulated DEGs were significantly enriched in the extracellular matrix disassembly, collagen catabolic process, chemokine-mediated signaling pathway and endopeptidase inhibitor activity. The KEGG pathway analysis revealed that downregulated DEGs were enriched in neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, hematopoietic cell lineage and vascular smooth muscle contraction, while upregulated DEGs were enriched in phototransduction. In addition, the top 10 hub genes and the most closely interacting modules of the top 3 proteins in the PPI network were screened. Finally, the independent prognostic value of each hub gene in LUAD patients was analyzed through the Kaplan-Meier plotter. Seven hub genes (ADCY4, S1PR1, FPR2, PPBP, NMU, PF4, and GCG) were closely correlated to overall survival time.
Conclusion: The discovery of these candidate genes and pathways reveals the etiology and molecular mechanisms of LUAD, providing ideas and guidance for the development of new therapeutic approaches to LUAD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of significant genes as prognostic markers and potential tumor suppressors in lung adenocarcinoma via bioinformatical analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 May 26;21(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08308-3. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34039311 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of UBB, RAC1, and ITGB1 Predicts Worse Prognosis among Nonsmoking Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma through Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 20;2020:2071593. doi: 10.1155/2020/2071593. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33134373 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Candidate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers Associated with Lung Adenocarcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jun 24;26:e922070. doi: 10.12659/MSM.922070. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32578582 Free PMC article.
-
Common gene signatures and key pathways in hypopharyngeal and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatic analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 16;99(42):e22434. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022434. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33080677 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of prognostic values of the transcription factor-CpG-gene triplets in lung adenocarcinoma: A narrative review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 16;101(50):e32045. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032045. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36550923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Expression Analysis of Biphasic Pleural Mesothelioma: New Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 10;12(3):674. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030674. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328227 Free PMC article.
-
In silico assessment of EpCAM transcriptional expression and determination of the prognostic biomarker for human lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC).Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Jul 19;27:101074. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101074. eCollection 2021 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 34345719 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and Identification of Four Prognostic Genes Related to Immune Infiltration and G-Protein Coupled Receptors Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 8;10:622251. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.622251. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33628734 Free PMC article.
-
The bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation of the carcinogenic role of EXO1 in lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 24;14:1492725. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1492725. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39777332 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the oncogenic role and prognostic value of CKS1B in human lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.Front Genet. 2025 Mar 17;16:1449466. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1449466. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40165937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Pirozynski M. 100 years of lung cancer. Respir Med 2006;100:2073–84. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018;553:446–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

