Influence of a Foot Insole for a Down Syndrome Patient with a Flat Foot: A Case Study
- PMID: 32384597
- PMCID: PMC7279166
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina56050219
Influence of a Foot Insole for a Down Syndrome Patient with a Flat Foot: A Case Study
Abstract
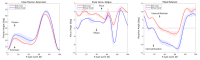
Background and Objectives: Patients with Down syndrome have many orthopedic problems including flat foot. Insertion of an insole for a flat foot provides support to the medial longitudinal arch; thus, insole therapy is often used to treat a flat foot. However, the influence of an insole insertion on the knee joint kinematics for a patient with Down syndrome is unknown. This study aimed to elucidate the influence of an insole for a flat foot on the knee kinematics during gait for a patient with Down syndrome. Materials and Methods: The subject was a 22-year-old male with Down syndrome who had a flat foot. The knee joint angle during the gait was measured using a 3D motion capture system that consisted of eight infrared cameras. Results: The gait analysis demonstrated a reduction in the knee flexion angle during double knee action. The knee valgus and tibial internal rotation angles also decreased during the loading response phase while wearing shoes that contained the insole. Conclusions: As the angle of the knee joint decreased during the gait, it was considered that the stability of the knee joint improved by inserting the insole. In particular, there was a large difference in the tibial internal rotation angle when the insole was inserted. It is thus hypothesized that the insole contributes to the rotational stability of the knee joint. This study suggests that knee stability may improve and that gait becomes more stable when a Down syndrome patient with a flat foot wears an insole.
Keywords: down syndrome; flat foot; gait analysis; insole; knee joint kinematics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials