Individual Fit Testing of Hearing-Protection Devices Based on Microphones in Real Ears among Workers in Industries with High-Noise-Level Manufacturing
- PMID: 32384734
- PMCID: PMC7246836
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17093242
Individual Fit Testing of Hearing-Protection Devices Based on Microphones in Real Ears among Workers in Industries with High-Noise-Level Manufacturing
Abstract
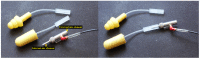
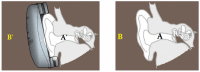
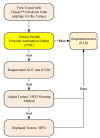
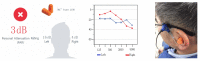
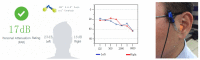
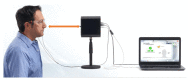
Hearing-protection devices (HPDs) are particularly important in protecting the hearing of workers. The aim of this study was to prevent hearing damage in workplaces in Taiwan. It was conducted to determine the actual sound attenuation of the personal attenuation rating (PAR) values when wearing HPDs via measurements from field microphones in workers' real ears (F-MIRE). Across 105 measurement trials for the Classic™ roll-down foam earplug HPDs worn by the workers, there were 23 cases of ineffective protection (including caution and fail); the proportion was 20% (including the first measurement and re-wear of HPDs after education and training). In addition, re-education and training in how to wear the HPDs was provided, improving wearing skills. A total of 29 testees wearing the Classic™ roll-down foam earplug HPDs failed to meet the pass standard for the first PAR test, and 6 of them improved and subsequently passed the PAR test. The improvement rate was 20%. These 23 testees switched to another HPD, namely Kneading-Free Push-Ins™ earplugs. From this group, 16 effective sound attenuation values were obtained, with an improvement rate of 70%. However, seven testees failed to pass the PAR test, and after education, training, and replacement of HPDs with different types, they still could not pass the PAR test. At that time, even if the UltraFit™ pre-molded earplugs were adopted again for wear and replacement, they were still unable to pass the PAR test. This HPD was eventually replaced with the PELTOR X4A Earmuff HPD and then tested again, with these HPDs finally passing the PAR test. In Taiwan, the use of fit testing has been increasing but it is not a common practice, and few studies on hearing-protection fit testing have been conducted in this country. The goal of this study was to gain more insight into the current hearing protection situation, including field attenuation of HPDs obtained by workers, the effects of training on improving the attenuation of HPDs after F-MIRE measurements, and the awareness of hearing health and motivation on the use of HPDs in a high-noise-level environment.
Keywords: field microphone in real ear (F-MIRE); hearing-protection device (HPD); noise exposure; personal attenuation rating (PAR); pre-workforce education.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variability of real-world hearing protector attenuation measurements.Ann Occup Hyg. 2006 Oct;50(7):679-91. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/mel025. Epub 2006 Jun 16. Ann Occup Hyg. 2006. PMID: 16782739
-
[Research on the protective effects and influencing factors of hearing protection device in different industries].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2025 Jul 20;43(7):508-512. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121094-20240424-00186. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40764241 Chinese.
-
[Measurement and evaluation of personal attenuation rating before and after the training of the noise-exposed workers wearing foam earplugs].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 20;42(8):589-593. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121094-20230817-00033. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39223044 Chinese.
-
Evaluating Earplug Performance over a 2-Hour Work Period with a Fit-Test System.Semin Hear. 2023 Jun 1;44(4):470-484. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1769586. eCollection 2023 Nov. Semin Hear. 2023. PMID: 37818150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individual fit-testing of earplugs: a review of uses.Noise Health. 2011 Mar-Apr;13(51):152-62. doi: 10.4103/1463-1741.77216. Noise Health. 2011. PMID: 21368441 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Earplugs in Preventing Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in an Auto Parts Factory in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 5;18(13):7190. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18137190. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34281127 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing protection field attenuation estimation systems and associated training for reducing workers' exposure to noise.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 17;5(5):CD015066. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015066.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38757544 Free PMC article.
-
A Tester to Evaluate the Correct Placement of Earplugs.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 11;19(14):8482. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19148482. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35886333 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Hearing Protection: Evaluating Innovative Training Modalities for Optimal Fitting Outcomes.Med Lav. 2025 Jun 17;116(3):16606. doi: 10.23749/mdl.v116i3.16606. Med Lav. 2025. PMID: 40536299 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Martínez L.F. Can You Hear Me Now: Occupational Hearing Loss, 2004-2010, U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Monthly Lab. Rev. 2012;135:48.
-
- Occupational Safety and Health administration OSHA (OSHA) Overview of the Reporting Statistics in 2008 about Occupational Diseases from the National Diagnosis and Treatment Network for Occupational Diseases and Injuries. OSHA, Ministry of Labor Republic of China (Taiwan); Taipei, Taiwan: 2018.
-
- Institute of Labor, Occupational Safety and Health (ILOSH) Developing an In-situ Measuring and Evaluation Model for Noise Control in Domestic Industries, Annual Research Project (ILOSH104-H312) ILOSH Ministry of Labor Republic of China (Taiwan); Taipei, Taiwan: 2016.
-
- Institute of Labor, Occupational Safety and Health (ILOSH) Study on Implementation Status and Development Strategy for Hearing Conservation Program, 2015 Annual Research Project (ILOSH104-H313) ILOSH, Ministry of Labor Republic of China (Taiwan); Taipei, Taiwan: 2016.
-
- Ministry of Labor (Taiwan) Occupational Safety and Health Act. Ministry of Labor Republic of China (Taiwan); Taipei, Taiwan: 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

