Comparative effectiveness of antitumour necrosis factor agents, biologics with an alternative mode of action and tofacitinib in an observational cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Switzerland
- PMID: 32385143
- PMCID: PMC7299517
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001174
Comparative effectiveness of antitumour necrosis factor agents, biologics with an alternative mode of action and tofacitinib in an observational cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Switzerland
Abstract
Background: Multiple biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying rheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) are approved for the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), including TNF inhibitors (TNFi), bDMARDs with other modes of action (bDMARD-OMA) and Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi). Combination of b/tsDMARDs with conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) is recommended, yet monotherapy is common in practice.
Objective: To compare drug maintenance and clinical effectiveness of three alternative treatment options for RA management.
Methods: This observational cohort study was nested within the Swiss RA Registry. TNFi, bDMARD-OMA (abatacept or anti-IL6 agents) or the JAKi tofacitinib (Tofa) initiated in adult RA patients were included. The primary outcome was overall drug retention. We further analysed secondary effectiveness outcomes and whether concomitant csDMARDs modified effectiveness, adjusting for potential confounding factors.
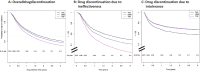
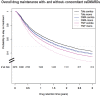
Results: 4023 treatment courses of 2600 patients were included, 1862 on TNFi, 1355 on bDMARD-OMA and 806 on Tofa. TNFi was more frequently used as a first b/tsDMARDs, at a younger age and with shorter disease duration. Overall drug maintenance was significantly lower with TNFi compared with Tofa [HR 1.29 (95% CI 1.14 to 1.47)], but similar between bDMARD-OMA and Tofa [HR 1.09 (95% CI 0.96 to 1.24)]. TNFi maintenance was decreased when prescribed without concomitant csDMARDs [HR: 1.27 (95% CI 1.08 to 1.49)], while no difference was observed for bDMARD-OMA or Tofa maintenance with respect to concomitant csDMARDs.
Conclusion: Tofa drug maintenance was comparable with bDMARDs-OMA and somewhat higher than TNFi. Concomitant csDMARDs appear to be required for optimal effectiveness of TNFi, but not for bDMARD-OMA or Tofa.
Keywords: abatacept; biological therapies; comparative effectiveness research; rheumatoid arthritis; tocilizumab; tumour necrosis alpha inhibitors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Yes, there are competing interests for one or more authors and I have provided a Competing Interests statement in my manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Courvoisier D, Mongin D, Hetland M, et al. . FRI0110 The impact of seropositivity on the effectiveness of abatacept versus TNF inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Real life data from several european registries (THE PAN-ABA STUDY). Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:599–600.
-
- Lauper K, Nordstrom DC, Pavelka K, et al. . Comparative effectiveness of tocilizumab versus TNF inhibitors as monotherapy or in combination with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis after the use of at least one biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug: analyses from the pan-European TOCERRA register collaboration. Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:1276–82.10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212845 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buckley F, Finckh A, Huizinga TW, et al. . Comparative efficacy of novel DMARDs as monotherapy and in combination with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to conventional DMARDs: a network meta-analysis. J Manag Care Spec Pharm 2015;21:409–23.10.18553/jmcp.2015.21.5.409 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
