Risk of Serious Falls Between Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Nationwide Population-based Cohort Study
- PMID: 32385311
- PMCID: PMC7211016
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-64698-7
Risk of Serious Falls Between Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Nationwide Population-based Cohort Study
Abstract
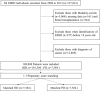
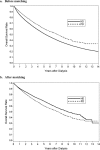
The association between serious falls and dialysis modality [hemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD)] is unclear. A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study with 127,823 end-stage renal disease patients aged over 18 years was conducted with the unmatched cohort of 101,304 HD and 7,584 PD patients retrieved from Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database during 2000-2013. A total of 7,584 HD and 7,584 PD patients matched at 1:1 ratio by propensity score were enrolled to the study. Serious falls were defined by the diagnostic codes, E code, and image studies. Cox regression model and competing-risk model were used for statistical analysis. HD patients were older and had more comorbidities at baseline than PD patients. After matching and adjustment, HD patients had a higher risk of serious falls than PD patients [sHR 1.27 (95% CI 1.06-1.52)]. Females, elders, a history of falls before dialysis, comorbidity with stroke or visual problems, using diuretics, α-blockers, and mydriatics were associated with higher risks of serious falls among dialysis patients. The risk of serious falls was higher in HD patients than PD patients. Health professionals should create age-friendly environments, reduce unnecessary medications, and raise patients' awareness of falls in daily life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of the risk of congestive heart failure-related hospitalizations in patients receiving hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis - A retrospective propensity score-matched study.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 1;14(10):e0223336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223336. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31574134 Free PMC article.
-
Greater risk of hip fracture in hemodialysis than in peritoneal dialysis.Osteoporos Int. 2014 May;25(5):1513-8. doi: 10.1007/s00198-014-2632-6. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Osteoporos Int. 2014. PMID: 24557014
-
Dialysis Mode and Associated Outcomes in Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease and Atrial Fibrillation: A 14-Year Nationwide Cohort Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Jun 15;10(12):e019596. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019596. Epub 2021 Jun 2. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34075777 Free PMC article.
-
Dialysis Modality and Mortality in the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):983-93. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05160514. Epub 2015 May 4. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25941194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peritoneal dialysis patient selection from a comorbidity perspective.Semin Dial. 2022 Jan;35(1):25-39. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12927. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Semin Dial. 2022. PMID: 33094512 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and risk factors of falls in people on hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2485375. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2485375. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40204427 Free PMC article.
-
Peritoneal dialysis versus haemodialysis for people commencing dialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 20;6(6):CD013800. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013800.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38899545 Free PMC article.
-
Signatures of Gait Movement Variability in CKD Patients Scheduled for Hemodialysis Indicate Pathological Performance Before and After Hemodialysis: A Prospective, Observational Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 28;8:702029. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.702029. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34395481 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with nursing diagnoses in chronic kidney patients: a cross-sectional study.Rev Cuid. 2021 Aug 20;12(3):e2160. doi: 10.15649/cuidarte.2160. eCollection 2021 Sep-Dec. Rev Cuid. 2021. PMID: 40115227 Free PMC article.
-
Trauma-related falls in an urban geriatric population: predictive risk factors for poorer clinical outcomes.Inj Epidemiol. 2023 Jan 30;10(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40621-023-00418-9. Inj Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 36717881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rossier A, Pruijm M, Hannane D, Burnier M, Teta D. Incidence, complications and risk factors for severe falls in patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation: official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association. 2012;27:352–357. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr326. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

