Noncalcified plaque burden quantified from coronary computed tomography angiography improves prediction of side branch occlusion after main vessel stenting in bifurcation lesions: results from the CT-PRECISION registry
- PMID: 32385529
- PMCID: PMC7806530
- DOI: 10.1007/s00392-020-01658-1
Noncalcified plaque burden quantified from coronary computed tomography angiography improves prediction of side branch occlusion after main vessel stenting in bifurcation lesions: results from the CT-PRECISION registry
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the incremental value of quantitative plaque features measured from computed tomography angiography (CTA) for predicting side branch (SB) occlusion in coronary bifurcation intervention.
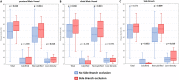
Methods: We included 340 patients with 377 bifurcation lesions in the post hoc analysis of the CT-PRECISION registry. Each bifurcation was divided into three segments: the proximal main vessel (MV), the distal MV, and the SB. Segments with evidence of coronary plaque were analyzed using semi-automated software allowing for quantitative analysis of coronary plaque morphology and stenosis. Coronary plaque measurements included calcified and noncalcified plaque volumes, and corresponding burdens (respective plaque volumes × 100%/vessel volume), remodeling index, and stenosis.
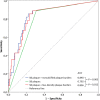
Results: SB occlusion occurred in 28 of 377 bifurcation lesions (7.5%). The presence of visually identified plaque in the SB segment, but not in the proximal and distal MV segments, was the only qualitative parameter that predicted SB occlusion with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.792. Among quantitative plaque parameters calculated for the SB segment, the addition of noncalcified plaque burden (AUC 0.840, p = 0.003) and low-density plaque burden (AUC 0.836, p = 0.012) yielded significant improvements in predicting SB occlusion. Using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, optimal cut-offs for noncalcified plaque burden and low-density plaque burden were > 33.6% (86% sensitivity and 78% specificity) and > 0.9% (89% sensitivity and 73% specificity), respectively.
Conclusions: CTA-derived noncalcified plaque burden, when added to the visually identified SB plaque, significantly improves the prediction of SB occlusion in coronary bifurcation intervention.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03709836 registered on October 17, 2018.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Coronary bifurcation; Coronary computed tomography angiography; Percutaneous coronary intervention; Plaque burden.
Conflict of interest statement
Mr. Sebastien Cadet, Dr. Piotr J. Slomka, and Dr. Damini Dey received software royalties from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center. The remaining authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Accuracy of RESOLVE score derived from coronary computed tomography versus visual angiography to predict side branch occlusion in percutaneous bifurcation intervention.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2020 May-Jun;14(3):258-265. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2020. PMID: 31806391
-
Visually Estimated RESOLVE Score Based on Coronary Computed Tomography to Predict Side Branch Occlusion in Percutaneous Bifurcation Intervention.J Thorac Imaging. 2021 May 1;36(3):189-196. doi: 10.1097/RTI.0000000000000570. J Thorac Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33464008
-
Plaque morphology predictors of side branch occlusion after provisional stenting in coronary bifurcation lesion: Results of optical coherence tomography bifurcation study (ORBID).Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2017 Feb 1;89(2):259-268. doi: 10.1002/ccd.26524. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2017. PMID: 27029714
-
Management of calcified coronary artery bifurcation lesions.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021 Jun 1;97(7):1407-1416. doi: 10.1002/ccd.29148. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021. PMID: 32776696 Review.
-
Impact of Side-Branch Predilation on Angiographic Outcomes in Non-Left Main Coronary Bifurcation Lesions.J Invasive Cardiol. 2020 Feb;32(2):42-48. doi: 10.25270/jic/19.00235. Epub 2020 Jan 20. J Invasive Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31958071
Cited by
-
Predictors and Biomarkers of Subclinical Leaflet Thrombosis after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 21;9(11):3742. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113742. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33233321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving Role of Coronary CT Angiography in Coronary Angiography and Intervention: A State-of-the-Art Review.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024 Dec;26(12):1347-1357. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02144-0. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39412596 Review.
-
Multislice computerized tomography coronary angiography can be a comparable tool to intravascular ultrasound in evaluating "true" coronary artery bifurcations.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Nov 6;10:1292517. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1292517. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 38028491 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of side branch occlusion in bifurcational lesions during percutaneous coronary interventions by preprocedural coronary computed tomography using the CT bifurcation score.Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2023 Jun;19(2):135-141. doi: 10.5114/aic.2023.129212. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2023. PMID: 37465628 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Cardiac Imaging in the Assessment of Aortic Stenosis.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 May 14;10(5):216. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10050216. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37233183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- He Y, Zhang D, Yin D, et al. Development and validation of a risk scoring system based on baseline angiographic results by visual estimation for risk prEdiction of side-branch OccLusion in coronary bifurcation InterVEntion: The baseline V-RESOLVE score. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;93(S1):810–817. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28068. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

