Whole genome sequencing and antibiotic diffusion assays, provide new insight on drug resistance in the genus Pedobacter
- PMID: 32386210
- PMCID: PMC7254926
- DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiaa088
Whole genome sequencing and antibiotic diffusion assays, provide new insight on drug resistance in the genus Pedobacter
Abstract
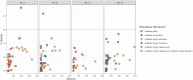
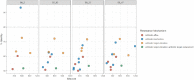
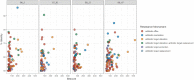
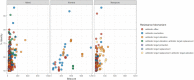
A total of four strains of the 'environmental superbug' Pedobacter isolated from sludge produced at Norwegian drinking water treatment plants, were characterized by whole genome sequencing and antibiotic susceptibility assays. As with previous studies on members of this genus, we found that the isolates were multi-drug resistant, and that this resistance included clinically important beta-lactams, aminoglycosides and the fluoroquinolone ciprofloxacin. Using the minION sequencing platform (Oxford Nanopore Technologies) combined with HiSeq PE150 Illumina sequencing data, the four isolates were assembled into genomes of single contigs. Analysis of the genomes revealed potential genetic factors possibly underlying some of the specific resistances observed. Metallo-beta-lactamase activity was detected in one isolate, and the same isolate contained a putative metallo-betalactamase gene resembling pedo-2. Furthermore, several genes related to multidrug efflux systems were found using the resistance database CARD. Additionally, the present study extends our knowledge on the phylogeny of this genus, adding four new genomes to the existing 50.
Keywords: Pedobacter spp; antimicrobial resistance; drinking water; environmental microbiology; minION sequencing.
© FEMS 2020.
Figures

References
-
- Aendekerk S, Diggle SP, Song Z et al. .. The MexGHI-OpmD multidrug efflux pump controls growth, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa via 4-quinolone-dependent cell-to-cell communication. Microbiology. 2005;151(Pt 4):1113–25. - PubMed
-
- Baker-Austin C, Wright MS, Stepanauskas R et al. .. Co-selection of antibiotic and metal resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2006;14:176–82. - PubMed
-
- Bengoechea JA, Skurnik M. Temperature-regulated efflux pump/potassium antiporter system mediates resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Yersinia. Mol Microbiol. 2000;37:67–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

