Enhanced electrocardiographic monitoring of patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019
- PMID: 32387247
- PMCID: PMC7200355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.04.047
Enhanced electrocardiographic monitoring of patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019
Abstract
Background: Many of the drugs being used in the treatment of the ongoing pandemic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are associated with QT prolongation. Expert guidance supports electrocardiographic (ECG) monitoring to optimize patient safety.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to establish an enhanced process for ECG monitoring of patients being treated for COVID-19.
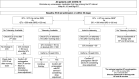
Methods: We created a Situation Background Assessment Recommendation tool identifying the indication for ECGs in patients with COVID-19 and tagged these ECGs to ensure prompt over reading and identification of those with QT prolongation (corrected QT interval > 470 ms for QRS duration ≤ 120 ms; corrected QT interval > 500 ms for QRS duration > 120 ms). This triggered a phone call from the electrophysiology service to the primary team to provide management guidance and a formal consultation if requested.
Results: During a 2-week period, we reviewed 2006 ECGs, corresponding to 524 unique patients, of whom 103 (19.7%) met the Situation Background Assessment Recommendation tool-defined criteria for QT prolongation. Compared with those without QT prolongation, these patients were more often in the intensive care unit (60 [58.3%] vs 149 [35.4%]) and more likely to be intubated (32 [31.1%] vs 76 [18.1%]). Fifty patients with QT prolongation (48.5%) had electrolyte abnormalities, 98 (95.1%) were on COVID-19-related QT-prolonging medications, and 62 (60.2%) were on 1-4 additional non-COVID-19-related QT-prolonging drugs. Electrophysiology recommendations were given to limit modifiable risk factors. No patient developed torsades de pointes.
Conclusion: This process functioned efficiently, identified a high percentage of patients with QT prolongation, and led to relevant interventions. Arrhythmias were rare. No patient developed torsades de pointes.
Keywords: COVID-19; ECG; Hydroxychloroquine; QT prolongation; Torsades de pointes.
© 2020 Heart Rhythm Society. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
COVID-19 treatments, QT interval, and arrhythmic risk: The need for an international registry on arrhythmias.Heart Rhythm. 2020 Sep;17(9):1423-1424. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.05.024. Epub 2020 May 26. Heart Rhythm. 2020. PMID: 32470627 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gao J., Tian Z., Yang X. Breakthrough: chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci Trends. 2020;14:72–73. - PubMed
-
- Fintelman-Rodrigues N, Sacramento CQ, Lima CR, et al. Atazanavir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and pro-inflammatory cytokine production [published online ahead of print April 6, 2020]. bioRxiv. 10.1101/2020.04.04.020925. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

