COVID-19: The first documented coronavirus pandemic in history
- PMID: 32387617
- PMCID: PMC7199674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.04.007
COVID-19: The first documented coronavirus pandemic in history
Abstract
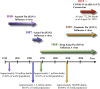
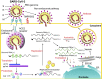
The novel human coronavirus disease COVID-19 has become the fifth documented pandemic since the 1918 flu pandemic. COVID-19 was first reported in Wuhan, China, and subsequently spread worldwide. The coronavirus was officially named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses based on phylogenetic analysis. SARS-CoV-2 is believed to be a spillover of an animal coronavirus and later adapted the ability of human-to-human transmission. Because the virus is highly contagious, it rapidly spreads and continuously evolves in the human population. In this review article, we discuss the basic properties, potential origin, and evolution of the novel human coronavirus. These factors may be critical for studies of pathogenicity, antiviral designs, and vaccine development against the virus.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Pandemic; SARS-COV-2.
© 2020 Chang Gung University. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous