Application of 9.4T MRI in Wilson Disease Model TX Mice With Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping to Assess Copper Distribution
- PMID: 32390811
- PMCID: PMC7189732
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00059
Application of 9.4T MRI in Wilson Disease Model TX Mice With Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping to Assess Copper Distribution
Abstract
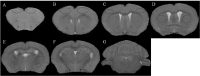
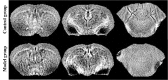
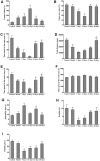
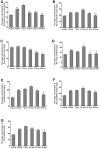
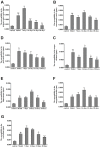
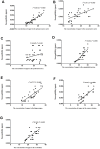
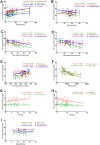
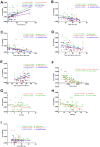
In the current study, we used 9.4-tesla magnetic resonance imaging (9.4T MRI) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) to investigate the distribution of copper in the brain samples of a murine model of Wilson's disease (WD) following penicillamine (PCA) treatment. We also evaluated if the distribution of copper in the brain samples of mice was correlated with behavioral symptoms. Results from the behavioral experiments showed that 7 days of PCA treatment decreased the total distance traveled in the open field and the number of rearing and climbing instances among the toxic milk (TX) mice as compared with model group. We also observed that the open arm ratio in the elevated plus-maze (EPM) was reduced, escape latency in the Barnes maze test was increased, and avoidance in the open field was enhanced in TX mice following 14 days of PCA treatment as compared with those in untreated TX mice. We found that PCA treatment for 21-28 days improved the cognitive abilities, exploratory behavior, and movement behavior of TX mice. The PCA-treated mice also exhibited varying degrees of magnetic susceptibilities in the cortex, corpus striatum, hippocampus, and amygdaloid nucleus across the treatment period. Low copper concentrations were found in all of the analyzed brain regions of PCA-treated mice after 21-28 days as compared with the model group (P < 0.05). However, copper concentrations were increased in the primary motor cortex and cerebellum at 7 days post-PCA treatment as compared with those in the model group (P < 0.05). After 14 days of PCA treatment, the copper concentrations in the sensorimotor cortex, corpus striatum, hippocampus, and amygdaloid nucleus were higher than those detected without treatment. The results from a Pearson's correlation analysis revealed that there was a significant (P < 0.05) correlation between copper concentrations and magnetic susceptibility in all of the brain regions that were analyzed. Therefore, our results indicate that copper concentration and magnetic susceptibility are associated with alterations in mood-related behavior, recognition memory, and movement behaviors in TX mice that are treated with PCA. The redistribution of copper in the TX mouse brain during PCA treatment may aggravate changes in behavioral performance.
Keywords: 9.4-Tesla magnetic resonance; TX mouse; Wilson disease; penicillamine; quantitative susceptibility mapping.
Copyright © 2020 Han, Dong, Xu, Rao, Shu, Li, Cheng, Wu, Yang, Han and Zhong.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

