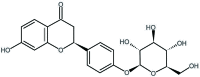
Liquiritin Alleviates Pain Through Inhibiting CXCL1/CXCR2 Signaling Pathway in Bone Cancer Pain Rat
- PMID: 32390832
- PMCID: PMC7193085
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00436
Liquiritin Alleviates Pain Through Inhibiting CXCL1/CXCR2 Signaling Pathway in Bone Cancer Pain Rat
Abstract
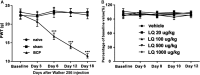
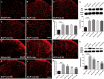
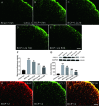
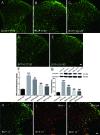
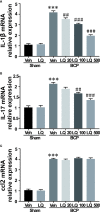
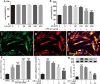
Bone cancer pain (BCP) is an intractable clinical problem, and lacked effective drugs for treating it. Recent research showed that several chemokines in the spinal cord are involved in the pathogenesis of BCP. In this study, the antinociceptive effects of liquiritin, which is an active component extracted from Glycyrrhizae Radix, were tested and the underlying mechanisms targeting spinal dorsal horn (SDH) were investigated. The BCP group displayed a significant decrease in the mechanical withdrawal threshold on days 6, 12, and 18 when compared with sham groups. Intrathecal administration of different doses of liquiritin alleviated mechanical allodynia in BCP rats. The results of immunofluorescent staining and western blotting showed that liquiritin inhibited BCP-induced activation of astrocytes in the spinal cord. Moreover, intrathecal administration of liquiritin effectively inhibited the activation of CXCL1/CXCR2 signaling pathway and production of IL-1β and IL-17 in BCP rats. In astroglial-enriched cultures, Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) elicited the release of chemokine CXCL1, and the release was decreased in a dose-dependent manner by liquiritin. In primary neurons, liquiritin indirectly reduced the increase of CXCR2 by astroglial-enriched-conditioned medium but not directly on the CXCR2 target site. These results suggested that liquiritin effectively attenuated BCP in rats by inhibiting the activation of spinal astrocytic CXCL1 and neuronal CXCR2 pathway. These findings provided evidence regarding the the antinociceptive effect of liquiritin on BCP.
Keywords: CXCL1; CXCR2; bone cancer pain; glia-neuron interaction; liquiritin; spinal cord.
Copyright © 2020 Ni, Xu, Xie, Fei, Deng, He, Wang, Liu, Zhu, Xu and Yao.
Figures


References
-
- Cao D. L., Zhang Z. J., Xie R. G., Jiang B. C., Ji R. R., Gao Y. J. (2014). Chemokine CXCL1 enhances inflammatory pain and increases NMDA receptor activity and COX-2 expression in spinal cord neurons via activation of CXCR2. Exp. Neurol. 261, 328–336. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.05.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

