Metabolomic Insights Into the Synergistic Effect of Biapenem in Combination With Xuebijing Injection Against Sepsis
- PMID: 32390846
- PMCID: PMC7189733
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00502
Metabolomic Insights Into the Synergistic Effect of Biapenem in Combination With Xuebijing Injection Against Sepsis
Abstract
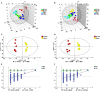
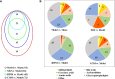
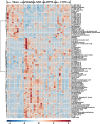
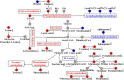
The drug combination of biapenem (BIPM) and xuebijing injection (XBJ) is commonly applied for the treatment of sepsis in China. However, the potential synergistic mechanism is still enigmatic. There have been no studies focused on the plasma metabolome alterations in sepsis after the intervention of this combination. In this work, an untargeted metabolomics approach was performed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry coupled with multivariate statistical analysis to provide new insights into the synergistic effect of BIPM in combination with XBJ. We characterized the metabolic phenotype of sepsis and described metabolic footprint changes in septic rats responding to XBJ and BIPM individually and in combination, in addition to histopathological and survival evaluation. A total of 91 potential biomarkers of sepsis were identified and 32 disturbed metabolic pathways were constructed. Among these biomarkers, 36 metabolites were reversely regulated by XBJ, mainly including glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, free fatty acids (FFAs), bile acids and acylcarnitines; 42 metabolites were regulated by BIPM, mainly including amino acids, glycerophospholipids, and acylcarnitines; 72 metabolites were regulated after XBJ-BIPM combination treatment, including most of the 91 potential biomarkers. The results showed that the interaction between XBJ and BIPM indeed exhibited a synergistic effect by affecting some key endogenous metabolites, 15 metabolites of which could not be regulated when XBJ or BIPM was used alone. Compared with Model group, 13, 22, and 27 metabolic pathways were regulated by XBJ, BIPM, and XBJ-BIPM combination, respectively. It suggested that many more endogenous metabolites and metabolic pathways were significantly regulated after combination treatment compared with XBJ or BIPM monotherapy. Metabolisms of lipids, amino acids, acylcarnitines, and bile acids were common pathways involved in the synergistic action of XBJ and BIPM. This study was the first to employ metabolomics to elucidate the synergistic effect and decipher the underlying mechanisms of BIPM in combination with XBJ against sepsis. The results provide some support for clinical application of antibiotics in combination with traditional Chinese medicines and have important implications for the treatment of sepsis in clinic.
Keywords: biapenem; drug combination; metabolomics; synergistic effect; xuebijing injection.
Copyright © 2020 Liu, Shi, Li, Zuo, Tang, Jing, Zhao, Xue, Zhou, Du, Zhang and Sun.
Figures


References
-
- Abdulkhalek S., Szewczuk M. R. (2013). Neu1 sialidase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 cross-talk regulates nucleic acid-induced endosomal TOLL-like receptor-7 and -9 activation, cellular signaling and pro-inflammatory responses. Cell Signal. 25, 2093–2105. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andries A., De Rechter S., Janssens P., Mekahli D., Van Schepdael A. (2018). Simultaneous determination of allantoin and adenosine in human urine using liquid chromatography – UV detection. J. Chromatogr. B. Anal. Technol. BioMed. Life Sci. 1096, 201–207. 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.08.026 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

