Shifting Valproic Acid to Levetiracetam in Women of Childbearing Age With Epilepsy: A Retrospective Investigation and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 32390936
- PMCID: PMC7193743
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00330
Shifting Valproic Acid to Levetiracetam in Women of Childbearing Age With Epilepsy: A Retrospective Investigation and Review of the Literature
Abstract
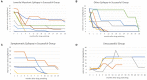
Objective: Valproic acid is the most high-risk teratogenic antiepileptic drug, and it may lead to fetal major congenital malformations. However, it is still used in women of childbearing age with epilepsy. The aim of this study was to report our experience of discontinuing or lowering valproic acid by adding levetiracetam, a low-risk teratogenic antiepileptic drug. Methods: We reviewed the medical records of childbearing age female patients with epilepsy who were treated with valproic acid initially and then switched to levetiracetam. The clinical profiles were recorded. The primary outcome was successful switching, which was defined as a decrease in the daily valproic acid dosage, after levetiracetam had been added. Results: Twenty-four female patients were enrolled (median age 22 years). The successful switching rate was 83.3% (20/24), and 55% (11/20) discontinued valproic acid after levetiracetam had been added. There were no significant differences between the successful and unsuccessful groups in etiology, electroencephalogram, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Pharmacoresistant to levetiracetam was much higher in the unsuccessful group (45 vs. 100%). The median switching duration was 19.5 months in the successful group. There were improvements in metrorrhagia and alopecia in all of the patients in the successful group after valproic acid had been tapered. Conclusions: Our experience supports switching valproic acid to levetiracetam in childbearing age women with epilepsy as an effective strategy to lower the teratogenic rate and adverse effects. A long switching period was noted in this study. We suggest starting early in childbearing age women with epilepsy.
Keywords: levetiracetam; major congenital malformation; pregnancy; switching; valproic acid; women with epilepsy.
Copyright © 2020 Kuo, Liu, Chou, Wang, Hung, Chou, Lin, Lan, Hsieh, Wang and Lin.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

