Multidisciplinary Diagnosis of Subcutaneous Soft Tissue Metastasis of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: A Case Report
- PMID: 32390944
- PMCID: PMC7188785
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00235
Multidisciplinary Diagnosis of Subcutaneous Soft Tissue Metastasis of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: A Case Report
Abstract
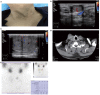
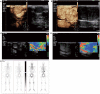
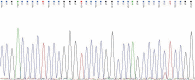
Background: Subcutaneous soft tissue metastasis of follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC) is rarely diagnosed before surgery for clinicians. Case Report: We present a case of a 67-year-old man with a history of FTC and papillary thyroid microcarcinoma for 5 years. Multiple protruding subcutaneous nodules of the neck were found and removed from the surface of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Ultrasound, computed tomography and technetium-99 m pertechnetate single-photon emission computed tomography of the neck were performed before the operation, which unfortunately indicated suspicious malignant lesions. Serum Tg was > 300 ng/ml (0.83-68.0 ng/ml), TSH was 36.580 uIU/ml (0.380-4.340 uIU/ml) and AbTg was negative. The pathologic diagnosis was metastatic FTC, invading the surrounding striated muscle, adipose tissue and vessels. Immunohistochemical staining revealed the tumor cells to be positive for thyroglobulin and TTF-1. The specimens of these nodules were further investigated for TERT promoter mutation and the result revealed mutated type (position g 1,295, 228 C>T). Conclusion: Preoperative diagnosis and prognostic prediction of metastatic FTC may be available through a combination of clinical, multimodal imaging and molecular genetic test (viz. multidisciplinary diagnosis). A long-term standardized follow-up is required for patients with a previous diagnosis of FTC.
Keywords: TERT promoter; case report; diagnosis; follicular thyroid carcinoma; metastasis.
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Nie and Fang.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

