Iron Limitation in Klebsiella pneumoniae Defines New Roles for Lon Protease in Homeostasis and Degradation by Quantitative Proteomics
- PMID: 32390954
- PMCID: PMC7194016
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00546
Iron Limitation in Klebsiella pneumoniae Defines New Roles for Lon Protease in Homeostasis and Degradation by Quantitative Proteomics
Abstract
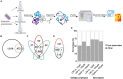
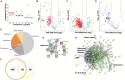
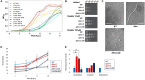
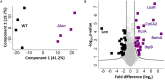
Nutrient adaptation is key in limiting environments for the promotion of microbial growth and survival. In microbial systems, iron is an essential component for many cellular processes, and bioavailability varies greatly among different conditions. In the bacterium, Klebsiella pneumoniae, the impact of iron limitation is known to alter transcriptional expression of iron-acquisition pathways and influence secretion of iron-binding siderophores, however, a comprehensive view of iron limitation at the protein level remains to be defined. Here, we apply a mass-spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics strategy to profile the global impact of iron limitation on the cellular proteome and extracellular environment (secretome) of K. pneumoniae. Our data define the impact of iron on proteins involved in transcriptional regulation and emphasize the modulation of a vast array of proteins associated with iron acquisition, transport, and binding. We also identify proteins in the extracellular environment associated with conventional and non-conventional modes of secretion, as well as vesicle release. In particular, we demonstrate a new role for Lon protease in promoting iron homeostasis outside of the cell. Characterization of a Lon protease mutant in K. pneumoniae validates roles in bacterial growth, cell division, and virulence, and uncovers novel degradation candidates of Lon protease associated with improved iron utilization strategies in the absence of the enzyme. Overall, we provide evidence of unique connections between Lon and iron in a bacterial system and suggest a new role for Lon protease in the extracellular environment during nutrient limitation.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; Lon protease; iron limitation; quantitative proteomics; secretome.
Copyright © 2020 Muselius, Sukumaran, Yeung and Geddes-McAlister.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

