Isolation and Characterization of Phosphorus Solubilizing Bacteria With Multiple Phosphorus Sources Utilizing Capability and Their Potential for Lead Immobilization in Soil
- PMID: 32390988
- PMCID: PMC7190802
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00752
Isolation and Characterization of Phosphorus Solubilizing Bacteria With Multiple Phosphorus Sources Utilizing Capability and Their Potential for Lead Immobilization in Soil
Abstract
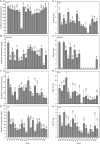
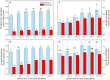
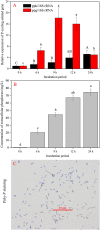
Phosphorus solubilizing bacteria (PSB) can promote the level of plant-absorbable phosphorus (P) in agro-ecosystems. However, little attention has been paid to PSB harboring abilities in utilizing multiple phosphorus sources and their potentials for heavy metal immobilization. In this study, we applied the strategy of stepwise acclimation by using Ca3(PO4)2, phytate, FePO4, and AlPO4 as sole P source. We gained 18 PSB possessing abilities of multiple P sources utilization, and these bacteria belonged to eight genera (Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, Massilia, Bacillus, Arthrobacter, Stenotrophomonas, Ochrobactrum, and Cupriavidus), and clustered to two apparent parts: Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria. The isolate of Acinetobacter pittii gp-1 presented good performance for utilizing Ca3(PO4)2, FePO4, AlPO4, and phytate, with corresponding P solubilizing levels were 250.77, 46.10, 81.99, and 7.91 mg/L PO4 3--P, respectively. The PSB A. pittii gp-1 exhibited good performance for solubilizing tricalcium phosphate in soil incubation experiments, with the highest values of water soluble P and available P were 0.80 and 1.64 mg/L, respectively. Additionally, the addition of A. pittii gp-1 could promote the immobilization of lead (Pb), and the highest Pb immobilization efficiency reached 23%. Simultaneously, we found the increases in abundances of both alkaline phosphatase gene (phoD) and β-propeller phytase gene (bpp) in strain gp-1 added soils. Besides, we observed the expression up-regulation of both pyrroloquinoline quinone gene (pqq) and polyphosphate kinases gene (ppk), with the highest relative expression levels of 18.18 and 5.23, respectively. We also found the polyphosphate particles using granule staining. To our knowledge, our findings first suggest that the solubilizing of tricalcium phosphate by phosphorus solubilizing bacterium belonging to Acinetobacter is coupled with the synthesis of polyphosphate. Taken together, A. pittii gp-1 could be a good candidate in improving soil fertility and quality.
Keywords: Acinetobacter pittii gp-1; P-cycling-related gene; Pb immobilization; multiple phosphorus source utilizing capacity; phosphorus solubilizing bacteria; ppk and pqq genes.
Copyright © 2020 Wan, Qin, Wu, Zuo, He, Tan, Wang and He.
Figures




References
-
- Bhattacharyya P., Nayak A. K., Shahid M., Tripathi R., Mohanty S., Kumar A., et al. (2015). Effects of 42-year long-term fertilizer management on soil phosphorus availability, fractionation, adsorption-desorption isotherm and plant uptake in flooded tropical rice. Crop J. 3 387–395. 10.1016/j.cj.2015.03.009 - DOI
-
- Chen Y., Fan J. B., Du L., Xu H., Zhang Q. H., He Y. Q. (2014). The application of phosphate solubilizing endophyte Pantoea dispersa triggers the microbial community in red acidic soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 84 235–244. 10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.05.014 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

