Direct activation of tRNA methyltransferase-like 1 (Mettl1) gene by thyroid hormone receptor implicates a role in adult intestinal stem cell development and proliferation during Xenopus tropicalis metamorphosis
- PMID: 32391142
- PMCID: PMC7197180
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-020-00423-1
Direct activation of tRNA methyltransferase-like 1 (Mettl1) gene by thyroid hormone receptor implicates a role in adult intestinal stem cell development and proliferation during Xenopus tropicalis metamorphosis
Abstract
Background: Thyroid hormone (T3) plays an important role in vertebrate development. Compared to the postembryonic development of uterus-enclosed mammalian embryos, T3-dependent amphibian metamorphosis is advantageous for studying the function of T3 and T3 receptors (TRs) during vertebrate development. The effects of T3 on the metamorphosis of anurans such as Xenopus tropicalis is known to be mediated by TRs. Many putative TR target genes have been identified previously. Among them is the tRNA methyltransferase Mettl1.
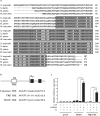
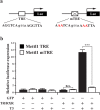
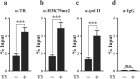
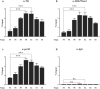
Results: We studied the regulation of Mettl1 gene by T3 during intestinal metamorphosis, a process involves near complete degeneration of the larval epithelial cells via apoptosis and de novo formation of adult epithelial stem cells and their subsequent proliferation and differentiation. We observed that Mettl1 was activated by T3 in the intestine during both natural and T3-induced metamorphosis and that its mRNA level peaks at the climax of intestinal remodeling. We further showed that Mettl1 promoter could be activated by liganded TR via a T3 response element upstream of the transcription start site in vivo. More importantly, we found that TR binding to the TRE region correlated with the increase in the level of H3K79 methylation, a transcription activation histone mark, and the recruitment of RNA polymerase II by T3 during metamorphosis.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that Mettl1 is activated by liganded TR directly at the transcriptional level via the TRE in the promoter region in the intestine during metamorphosis. Mettl1 in turn regulate target tRNAs to affect translation, thus facilitating stem cell formation and/or proliferation during intestinal remodeling.
Keywords: Anuran metamorphosis; Intestine; Methyltransferase; Stem cell; Thyroid hormone receptor; Xenopus tropicalis; tRNA.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lazar MA. Thyroid hormone receptors: multiple forms, multiple possibilities. Endocr Rev. 1993;14(2):184–193. - PubMed
-
- Yen PM. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(3):1097–1142. - PubMed
-
- Tata JR. Gene expression during metamorphosis: an ideal model for post-embryonic development. BioEssays. 1993;15(4):239–248. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y-B. Amphibian metamorphosis: from morphology to molecular biology. New York: Wiley; 1999.
-
- Hetzel BS. The story of iodine deficiency: an international challenge in nutrition. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1989.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

