Development and application of a rapid HPLC method for simultaneous determination of hyperoside, isoquercitrin and eleutheroside E in Apocynum venetum L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus
- PMID: 32391523
- PMCID: PMC7196217
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-020-00687-1
Development and application of a rapid HPLC method for simultaneous determination of hyperoside, isoquercitrin and eleutheroside E in Apocynum venetum L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus
Abstract
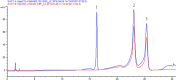
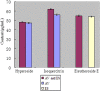
Apocynum venetum L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus have been used for hundreds of years to treat hypertension in China. In previous research, there was not a suitable quality control of method for the formulas of Apocynum venetum L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus. It is urgent and essential to develop modern analytical methods for Apocynum venetum L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus to ensure the quality of the formulas. A rapid approach for simultaneous determination of hyperoside, isoquercitrin and eleutheroside E in Apocynum venetum L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus by high-performance liquid chromatography with a diode array detector was described and validated. The full method validation, including the linearity, limits of detection and quantification, precision, repeatability, stability and recovery, was examined. All target components, including isomers of hyperoside and isoquercitrin, were baseline separated in 35 min. The developed method was sensitive, reliable and feasible. With this method, the optimal decoction conditions of Apocynum venetum L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus were selected, and their quality analysis was carried out. Furthermore, an herbal compatibility study of Apocynum venetum L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus based on detecting variations in the content of their active ingredients was performed by the developed HPLC method. It could be an alternative for the quantitative analysis of herbs that contain hyperoside, isoquercitrin or (and) eleutheroside E in the future.
Keywords: Eleutheroside E; Hyperoside; Isoquercitrin; Quality control.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsAll the authors listed in the manuscript have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Chan CO, Lau CC, Ng YF, Xu LJ, Chen SB, Chan SW, Mok DK. Discrimination between leave of Apocynum venetum and its adulterant, A. pictum based on antioxidant assay and chemical profiles combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Antioxidants. 2015;4:359–372. doi: 10.3390/antiox4020359. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
