Why do young people get cancer?
- PMID: 32391946
- PMCID: PMC7582786
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.28335
Why do young people get cancer?
Abstract
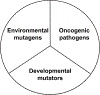
Oncologists and cancer biologists are frequently confronted by the question of what causes cancer? This is particularly vexing for cancers affecting children and young adults who have had limited exposure to environmental mutagens and the effects of aging. Here, I focus on a general framework of the causes of early-onset cancer development in children and young adults by relating inherited and constitutional cancer predisposition, oncogenic pathogens, and developmental mutations. This framework has implications not only for mechanistic investigation of young cancers, but should also clarify improved strategies for their treatment, screening, and potential prevention.
Keywords: oncogenes; oncology; pediatric hematology/oncology; tumor biology.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Strahm B, Malkin D. Hereditary cancer predisposition in children: genetic basis and clinical implications. Int J Cancer. 2006;119(9):2001–2006. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes WD. Inherited susceptibility to common cancers. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(20):2143–2153. - PubMed
-
- Ripperger T, Bielack SS, Borkhardt A, et al. Childhood cancer predisposition syndromes-A concise review and recommendations by the Cancer Predisposition Working Group of the Society for Pediatric Oncology and Hematology. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173(4):1017–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical